High blood pressure is a common chronic disease that increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure if not well-controlled. Beyond medication, lifestyle and diet play a crucial role in stabilizing blood pressure. Factors that make blood pressure difficult to control include a high-salt diet, excessive saturated fats, and insufficient fruit and vegetable intake.
Shrimp is rich in high-quality protein, low in fat, and provides minerals such as calcium, potassium, magnesium, selenium, and iodine. These nutrients benefit heart muscle function and nerve transmission. However, shrimp also contains relatively high cholesterol and can easily accumulate more salt during preparation methods like stir-frying, braising with high salt, or cooking with fish sauce. Improper shrimp consumption can increase sodium intake, leading to elevated blood pressure.
Individuals with high blood pressure can still eat shrimp if consumed in reasonable amounts and prepared correctly. It is advisable to eat one to two shrimp meals per week, with each serving consisting of approximately 80-100 g of fresh shrimp, totaling about 200 g of fresh shrimp weekly. Prioritize steaming, boiling, light grilling, or quick stir-frying with minimal oil and salt. Avoid dried shrimp dishes, salty braised shrimp, salted shrimp, or serving with salty dipping sauces, as these quickly increase sodium intake.
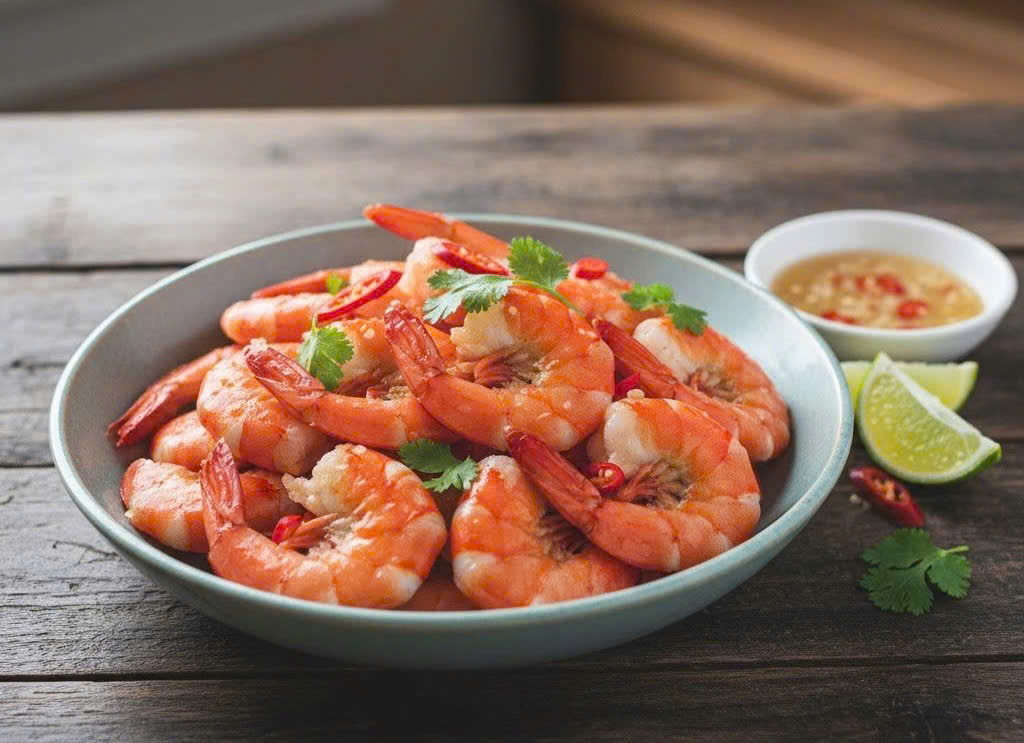 |
Patients with high blood pressure can eat about 200 g of fresh shrimp per week. *Trong Nghia*.
When consuming shrimp, patients must balance their overall diet. Incorporate plenty of green vegetables, whole grains, and potassium-rich fruits, while limiting processed foods, dipping sauces, pickled items, and alcoholic beverages. If co-existing conditions such as dyslipidemia, diabetes, or kidney disease are present, patients should consult their doctor to adjust protein and cholesterol intake accordingly.
Individuals with high blood pressure should monitor their blood pressure at home and undergo regular checks for blood lipids, blood sugar, and kidney function. Patients can seek consultations with cardiology or nutrition specialists for a comprehensive cardiovascular risk assessment, which helps in developing appropriate dietary and lifestyle plans to reduce complications during treatment. Natural essences like GDL-5 from South American sugarcane pollen, containing natural policosanol, can help regulate blood lipids and support high blood pressure control.
Master, Doctor Nguyen Anh Duy Tung
Specialist in Nutrition and Dietetics
Tam Anh General Clinic District 7
| Readers can submit nutrition questions here for doctor answers |