Answer:
Anxiety is a normal bodily reaction to stressful situations such as exams, job interviews, or changes in living environment. At this level, feelings of nervousness or tension typically appear for a short duration, gradually diminish once the event passes, and do not significantly affect daily life. The sympathetic nervous system naturally adjusts its activity, helping the body return to a balanced state.
Anxiety disorder occurs when feelings of fear and anxiety become uncontrollable and persist continuously, even without a clear reason. The brain, in this state, becomes "stuck" in an alert mode, making the individual feel uneasy and unable to relax. Symptoms of anxiety disorder are more pronounced, including a rapid heart rate, palpitations, trembling hands, shortness of breath, nausea, stomach pain, or dizziness. Some individuals experience panic attacks with feelings of suffocation, numbness, or fear of losing control.
Prolonged anxiety significantly affects quality of life, making it difficult for individuals to concentrate, reducing work performance, leading to social avoidance, and trapping them in a cycle of stress and insomnia. Without early detection and treatment, anxiety can easily progress to an anxiety disorder, which over time may lead to depression, heart rhythm disorders, digestive disorders, or impaired immune function.
The causes of anxiety disorder are diverse, ranging from chronic stress, psychological trauma, and work pressure to hormonal changes, lack of sleep, or caffeine abuse. Disruptions in serotonin neurotransmission and an imbalance in the nervous system also cause the body to overreact to normal stimuli.
You should seek medical attention if feelings of anxiety persist for more than two weeks, accompanied by persistent palpitations, insomnia, shortness of breath, headaches, chest pain, or difficulty concentrating. Individuals experiencing anxiety with abnormal symptoms such as panic attacks, sudden fear, numbness or weakness in the limbs, or dizziness should consult a neurologist to differentiate between normal anxiety and an anxiety disorder.
Depending on the severity of the condition, doctors may prescribe neurotransmitter-regulating medications combined with cognitive behavioral therapy, which helps patients change negative thought patterns. Patients may also be treated with transcranial magnetic stimulation technique. This non-invasive method uses magnetic waves to directly stimulate the cerebral cortex to regulate abnormal electrophysiological activity.
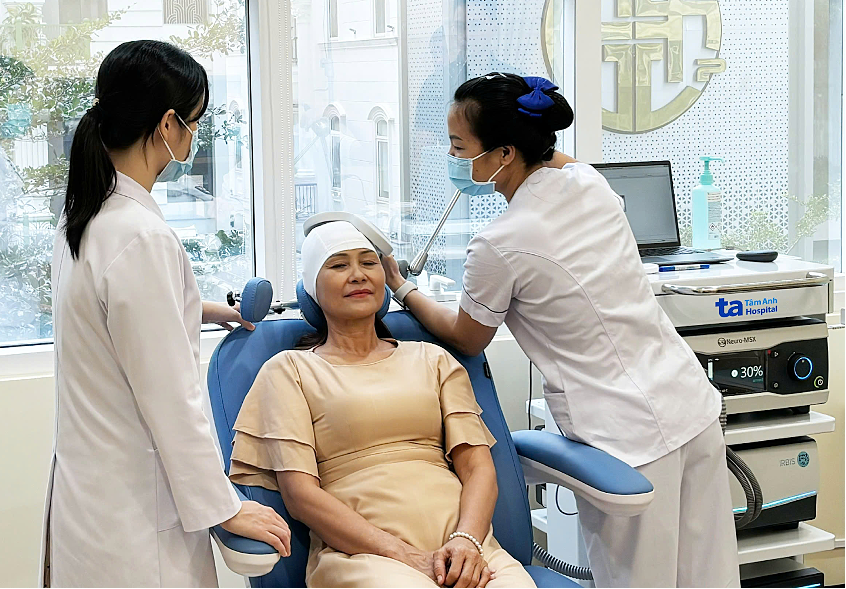 |
A doctor uses transcranial magnetic stimulation to treat a patient with anxiety disorder. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
This technique helps calm the brain regions that control emotions, supporting the reduction of anxiety, improving sleep, and stabilizing mood. Each treatment course lasts approximately 4-6 weeks; patients can resume normal activities immediately after a session and may not need medication or can reduce their dosage depending on the case. The method is individualized for each patient based on a brain navigation system, and it is safe for older adults and patients with underlying health conditions. The primary side effects are mild headaches or transient scalp numbness.
Maintaining a scientific lifestyle, getting enough sleep, limiting caffeine, and practicing deep breathing or meditation every day also contribute to stabilizing the nervous system and improving symptoms. Anxiety disorder can be effectively managed and treated if individuals proactively seek early examination, preventing the condition from prolonging and causing mental and physical complications.
Doctor Nguyen Huu Khanh
Center for Neuroscience
Tam Anh General Hospital, TP HCM
| Readers can send questions about neurological conditions here for doctors to answer. |