Body aches, inflammation, swelling, and redness in at least 4 joints at the same time can be a sign of polyarthritis. Doctor Ngo Tuan Anh, from the Department of Rheumatology at Tam Anh General Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City, explains that polyarthritis isn't a specific type of arthritis, but rather relates to various causes such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus.
The severity of polyarthritis depends on the condition, its cause, and the patient's healthcare practices. Without early diagnosis and effective management, the disease can progress significantly, leading to several complications.
Chronic pain: Polyarthritis is linked to some autoimmune diseases, which are not entirely curable. Patients may experience pain lasting over 3 months, with recurring episodes. Chronic pain can lead to mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
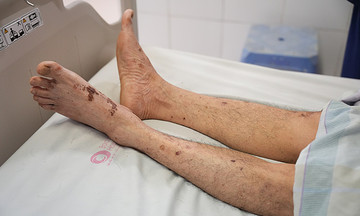
Joint deformity: Depending on the affected joint, patients may experience changes in their walking, standing, or sitting posture, impacting their mobility and daily activities.
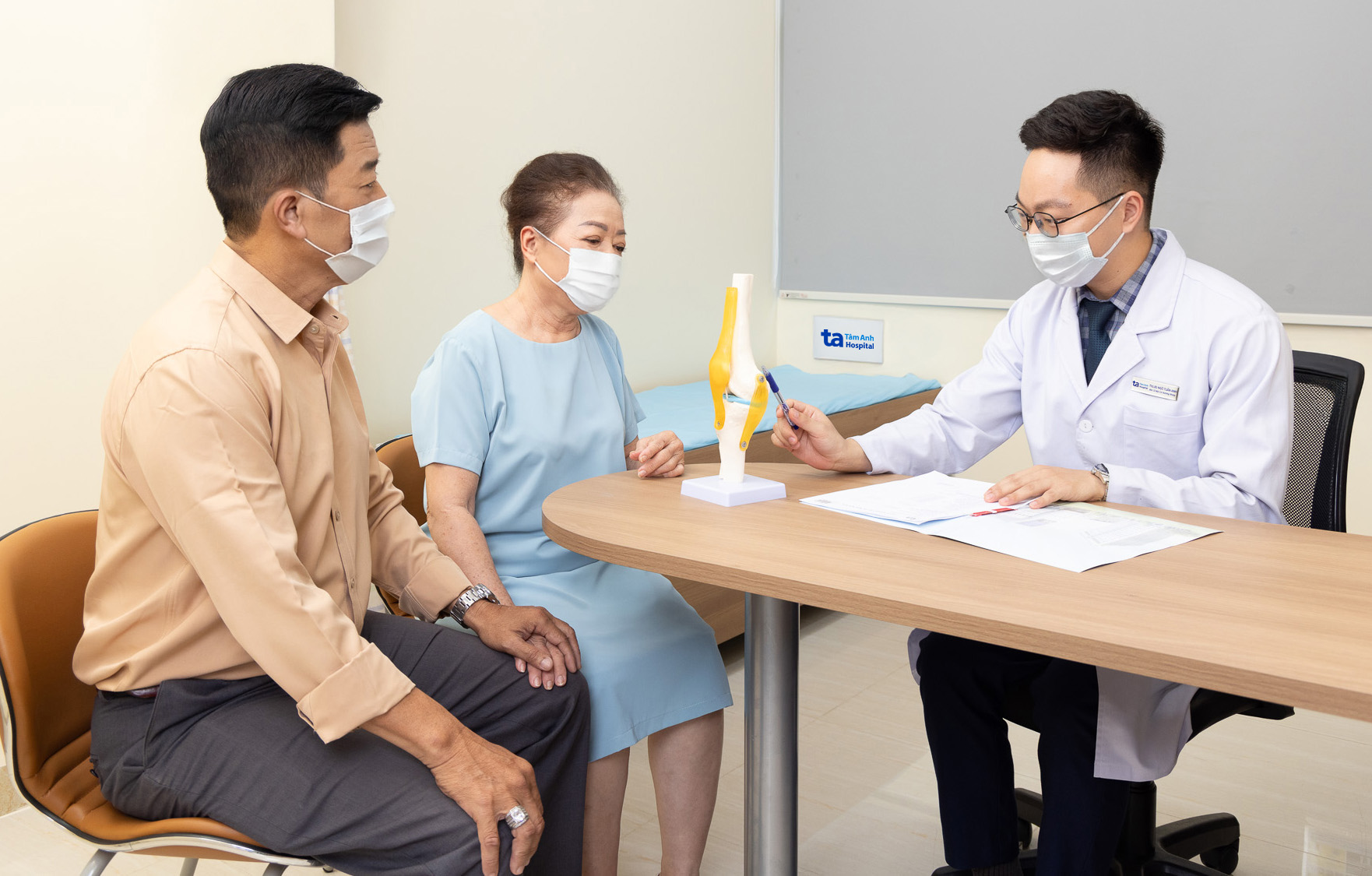 |
Doctor Tuan Anh explains a knee condition to a patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Doctor Tuan Anh explains a knee condition to a patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
Disability and loss of mobility: Severe arthritis can completely damage the bones and cartilage in the affected joint or lead to fractures. These complications increase the risk of disability and loss of mobility.
Systemic complications: Polyarthritis can affect other vital organs besides the musculoskeletal system, depending on the underlying cause. For example, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to complications in the lungs, heart, and eyes, while systemic lupus erythematosus can affect the kidneys, heart, lungs, and skin.
Most cases of polyarthritis are not completely curable. However, with proper management, the impact on daily life can be minimized, significantly reducing the risk of complications. Treatment options include oral or injectable medications. Joint injections offer rapid pain and inflammation relief, but overuse can cause side effects.
Regular exercise at an appropriate intensity improves musculoskeletal flexibility. Depending on individual abilities and preferences, patients can start with gentle exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling. Exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing stress on the joints.
If polyarthritis leads to severe osteoarthritis and complete loss of function, joint replacement surgery is an option. The type of artificial joint and surgical procedure vary depending on the affected joint. This invasive procedure replaces the damaged joint with a new artificial one, restoring mobility. At Tam Anh General Hospital, patients can typically walk again just 1-2 days after major joint replacements like knee or hip.
To manage polyarthritis and prevent complications, Doctor Tuan Anh advises patients to adhere to prescribed treatments, attend regular check-ups, and seek medical attention immediately if any unusual symptoms arise.
Phi Hong
| Readers can submit questions about musculoskeletal diseases here for doctors to answer. |