Traditional medicine practitioner Do Minh Tuan, from the Hanoi Oriental Medicine Association, states that the liver's function is to detoxify the body. Maintaining a healthy liver requires providing essential nutrients. Elevated liver enzymes indicate compromised liver function. To care for and protect this digestive organ, remember the principle: "Eat three bitter, avoid two sweet."
Bitter melon
Bitter melon, also known as the "gentleman's vegetable", retains its bitter taste whether stir-fried, boiled, or cooked with any food. Traditional medicine believes that raw bitter melon has cooling properties, while cooked bitter melon is warming. Consuming it raw in summer helps clear heat, while cooked bitter melon nourishes blood, strengthens the liver, and benefits the spleen and kidneys.
Research indicates that bitter melon can enhance the body's antioxidant system through intrinsic enzymes like catalase and superoxide dismutase. These compounds can prevent liver damage caused by alcohol consumption. Additionally, bitter melon effectively boosts liver immunity and supports normal liver function, attributed to its high vitamin C content.
Scientific evidence confirms that the bitter compounds in bitter melon promote bile secretion and liver detoxification. Therefore, incorporating this food into daily meals, perhaps as a salad, soup, or stir-fried with eggs, is advisable.
Bitter greens
Bitter greens possess a mildly bitter and sweet taste. They are rich in vitamins, fiber, plant protein, and other nutrients. They also provide essential trace elements such as calcium, phosphorus, zinc, and copper.
Regular consumption of bitter greens can strengthen the body's resistance, enhance immunity, and promote healthy brain and liver function.
Bitter tea
Drinking water is an excellent way to maintain health. It not only replenishes body fluids, boosts blood circulation, and promotes metabolism but also aids the digestive system in absorbing nutrients and eliminating waste. This reduces liver damage from metabolites and toxins. To protect the liver, consider drinking bitter herbal teas for liver nourishment, such as green tea, voi tea, or ginger tea.
Green tea and green tea extracts have liver-protective effects. This is due to the polyphenol compound epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which can significantly reduce markers of liver damage or inflammation. Drinking green tea can also prevent liver diseases like liver cancer, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and fatty liver. Ginger, for instance, protects the liver from harmful compounds induced by alcohol consumption.
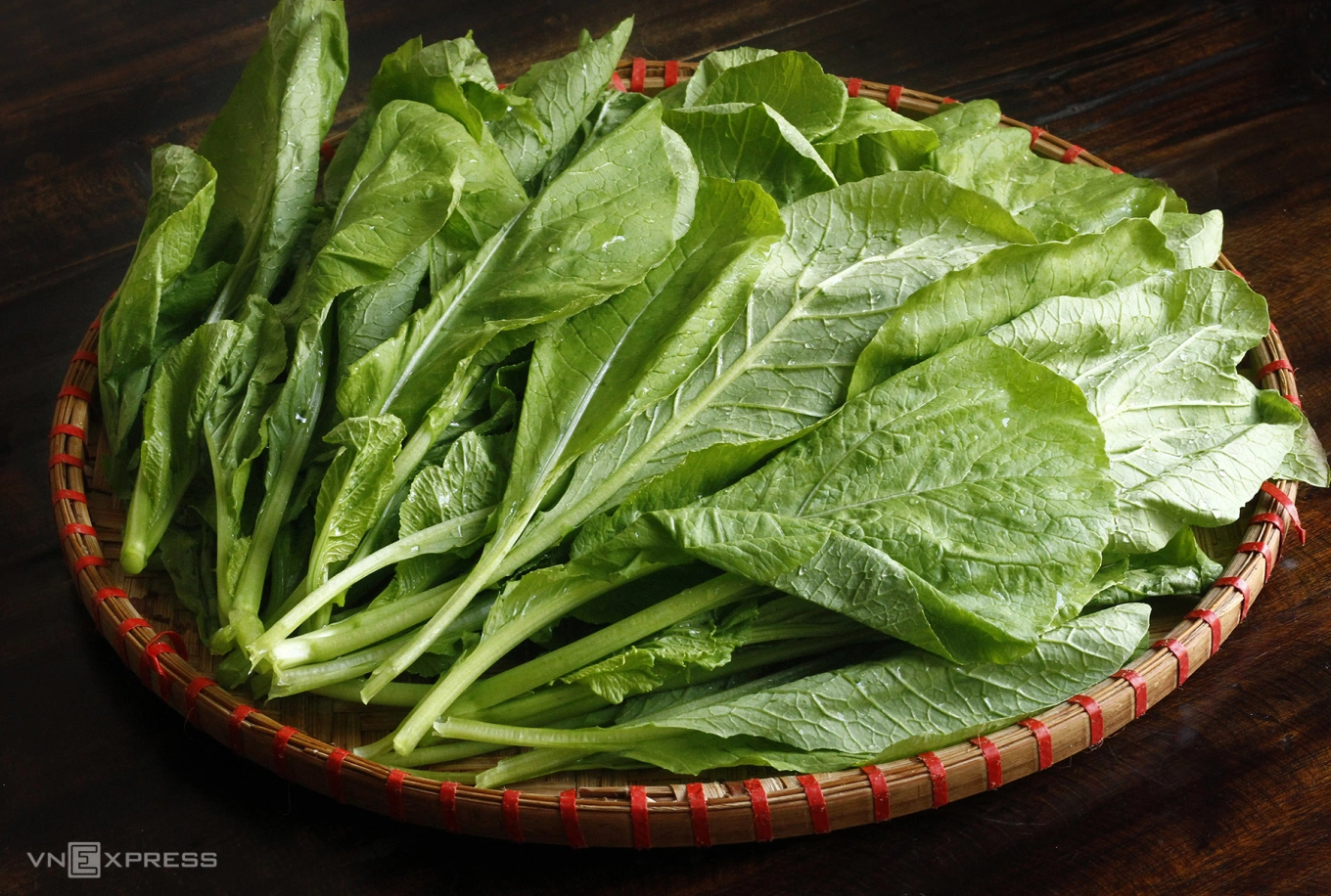 |
Bitter greens are good for the liver. Photo: Bui Thuy |
In contrast to bitter foods, sweet substances are highly detrimental to the liver. Sugars like sucrose, glucose, and fructose metabolize into glycogen, which is stored in the liver. When the body has an excess, this leads to an overload and conversion into accumulated fat, resulting in fatty liver. Two sweet foods particularly harmful to the liver are chocolate and milk tea.
Chocolate
Frequent chocolate consumption generates too much energy, causing obesity and increasing the burden on the intestines by stimulating excessive enzyme secretion. Chocolate also impacts sugar metabolism, adding strain to the liver and promoting the conversion of sugar into fat.
Milk tea
Most milk teas are made from artificial synthetic food ingredients. This beverage also contains high sugar levels, increasing the liver's burden. Milk tea also contains considerable starch, which reduces the body's excretion of water and sodium.
Regular consumption of these beverages increases the liver's burden, affecting its normal function and potentially causing inflammation and cirrhosis.
Beyond these two sweet foods, be mindful that consuming too much fruit, especially high-sugar varieties, is also not beneficial for the liver. Individuals with compromised liver function should consume fruits in moderation, avoiding overly sweet types.
Thuy Quynh