Hashimoto's disease (thyroiditis) is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks healthy tissues, including thyroid cells. Over time, this causes inflammation and reduces the thyroid gland's ability to produce thyroid hormones. While there is currently no cure for Hashimoto's disease, certain dietary changes can help manage the condition and improve thyroid function.
Emphasize foods that promote satiety and prevent inflammation
Beneficial diets for individuals with Hashimoto's disease include those that limit gluten or grains, the Mediterranean diet, the MIND diet which supports inflammation reduction, and lactose-free diets.
Patients should consume whole foods rich in nutrients and antioxidants such as polyphenols and phytosterols. These compounds help reduce inflammation, maintain a healthy weight, and enhance overall health. Conversely, a diet lacking these foods can have the opposite effect, triggering inflammation. When inflammation occurs, the body produces more antibodies, leading to increased autoimmune activity.
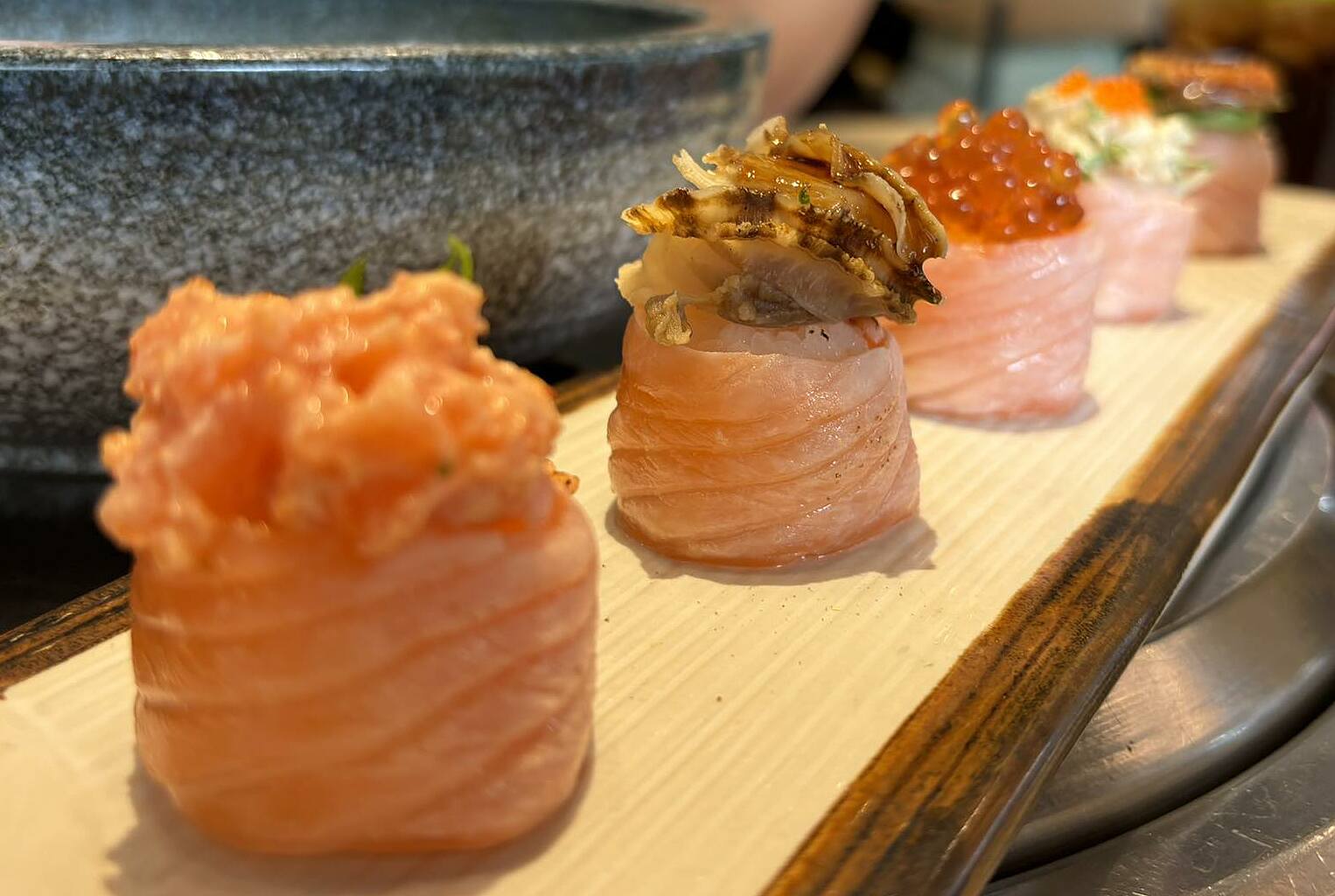 |
Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation. Photo: Anh Chi
To achieve these benefits, consider incorporating the following foods:
Juicy fruits: apples, cherries, oranges, grapes, citrus fruits, or avocados.
Vegetables: spinach, kale, tomatoes, broccoli, beets, carrots, and bell peppers.
Whole grains: oats, quinoa, whole wheat, brown rice, barley.
Legumes: lentils, kidney beans, pinto beans, navy beans, black beans.
Nuts and seeds: walnuts, peanuts, almonds, cashews, sunflower seeds, flaxseeds, chia seeds.
Fatty fish: salmon, mackerel, herring, sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that play a strong role in reducing inflammation and preventing recurrent thyroid inflammation symptoms.
Herbs and spices: turmeric, rosemary, paprika, basil, and saffron.
Supplementing with vitamin-rich foods
Certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, stabilize thyroid antibodies in the body and improve thyroid function. Selenium plays a crucial role in thyroid hormone synthesis and metabolism. Therefore, individuals with thyroiditis should supplement with selenium-rich foods like oysters, tuna, lobster, mackerel, and lean chicken.
Foods to avoid
While each Hashimoto's patient requires a personalized diet based on their health condition, it is generally advisable to limit certain food groups: high-sugar dishes; foods rich in animal fats such as beef, lamb, and pork; and fried foods. Refined grains like white bread, white rice, products made from white flour, and processed meats should also be avoided as they contain unhealthy fats, preservatives, and seasonings that can increase inflammation.
Patients should limit dairy products, high-salt foods, and iodine, as these can promote inflammation and negatively affect thyroid function. It is also advisable to limit raw consumption of broccoli, cabbage, brussels sprouts, and kale, as they are rich in goitrogens (compounds that can disrupt thyroid function if consumed in excess). Cooking these vegetables reduces these compounds, making them safer to consume.
Anh Chi (According to Healthline, Very Well Health)
| Readers can ask questions about endocrine diseases here for doctors to answer |