Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common condition that progresses silently without clear symptoms. However, experts believe daily lifestyle habits play a decisive role in preventing and controlling the disease.
If detected early, patients can fully improve liver function naturally, often without the need for medication.
What is NAFLD?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver of individuals who do not consume alcohol. The causes of NAFLD typically stem from metabolic factors.
NAFLD comprises two main stages. In the first stage, simple fatty liver, fat accumulates without causing inflammation and can be reversed through lifestyle changes. In the second stage, known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the liver begins to inflame, damaging cells, and can easily progress to cirrhosis or cancer if not treated promptly.
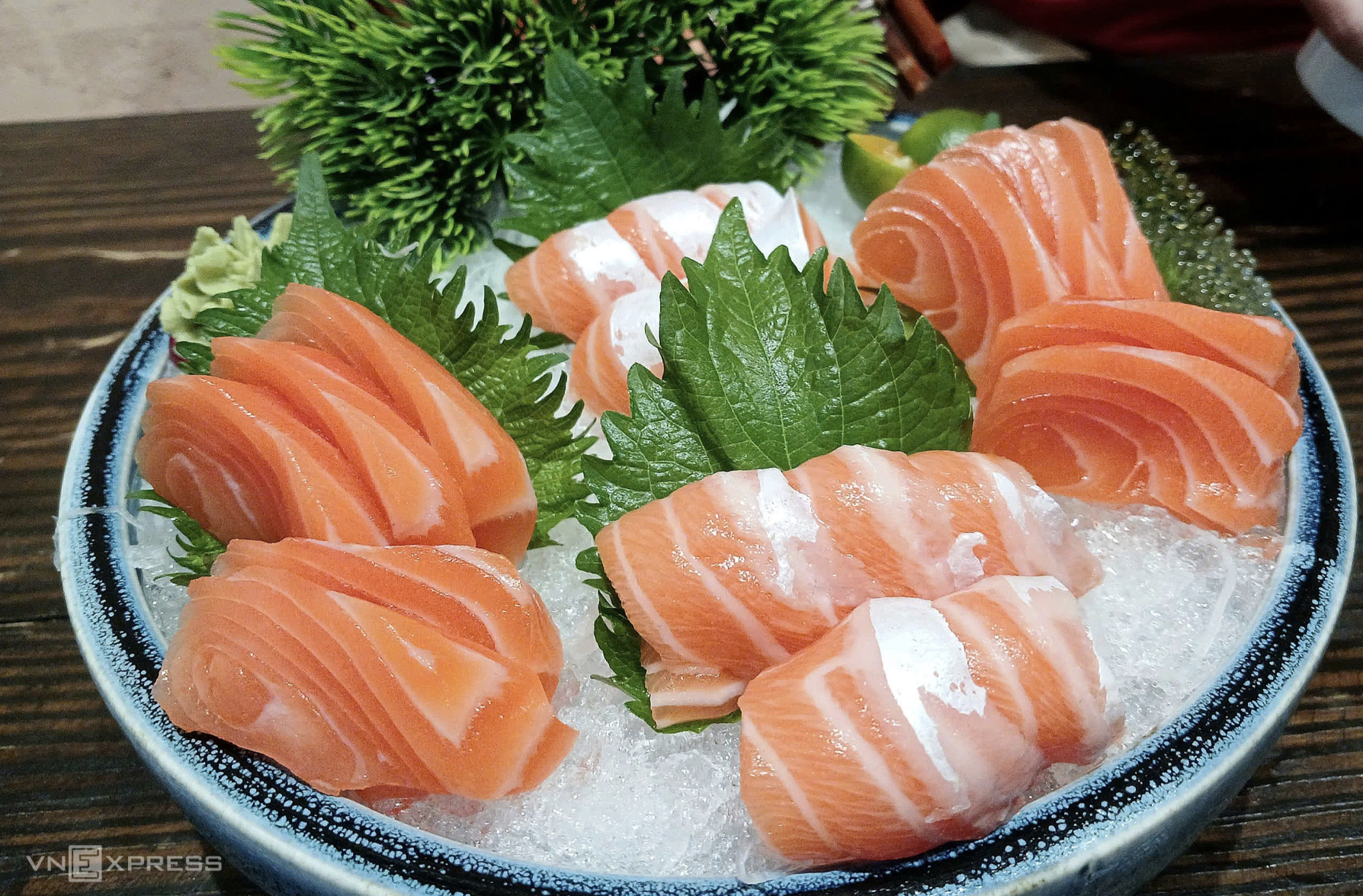 |
Fatty fish like salmon are rich in omega-3, which helps lower triglycerides and improve liver function. *Thi Ha* |
Three primary culprits harming the liver
Added sugar and sugary drinks
Excess sugar, especially fructose, causes fat accumulation in the liver and reduces insulin sensitivity. According to research by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the US, excessive consumption of added sugar is directly linked to elevated liver enzymes and promotes the progression of fatty liver disease.
Ultra-processed foods and refined carbohydrates
Fast food, packaged snacks, and refined grains contribute to increased liver fat. A study of 16,000 people revealed that those who consumed these foods frequently had an 18% higher risk of developing the disease.
Alcohol
Although NAFLD is "non-alcoholic", alcohol consumption still places additional stress on the liver. Numerous studies indicate that even moderate drinking can accelerate liver fibrosis and cause the disease to progress more rapidly.
Daily liver-supporting foods
Fiber
Vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains, rich in fiber, help reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and effectively reduce inflammation.
Omega-3
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3, which helps lower triglycerides, improves liver function, and is safe for individuals with NAFLD.
Polyphenols
Polyphenols, antioxidant compounds found in green tea, coffee, berries, turmeric, and dark chocolate, help reduce inflammation and protect liver cells from damage.
Build liver-protective habits
Eat two to three hours before bedtime
Individuals who eat three meals or fewer per day or fast overnight for 14 hours or more have a higher risk of NAFLD compared to those who eat more frequent meals, a study of 11,153 Americans indicated.
Drink enough water
Water helps the liver metabolize, detoxify, and nourish cells. People who drink plenty of water have a lower mortality risk when suffering from NAFLD.
Get enough sleep
Lack of sleep or disturbed sleep both increase liver fat, elevate liver enzymes, and contribute to insulin resistance. Going to bed and waking up at the same time daily, even on weekends, helps stabilize circadian rhythms and supports liver recovery.
Combining a healthy diet, supplementing with essential nutrients, maintaining positive lifestyle habits, and regular exercise creates a strong synergistic effect. Clinical research demonstrates that individuals who maintain both regular exercise and proper nutrition show the best improvements in liver fat and metabolic markers.
Huong Giang (According to Times of India)