Fatty liver develops when excess fat accumulates in the liver. Increased fat accumulation leads to more severe disease. While initially asymptomatic, it weakens the liver over time. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and physical activity, can prevent its progression. Patients should implement these changes gradually to ensure long-term adherence and success.
Engage in appropriate exercise
Individuals who are overweight or obese should prioritize weight loss to manage fatty liver. Losing weight effectively reduces liver fat, prevents inflammation, and minimizes liver scarring. Regular exercise is essential for achieving a healthy weight and stimulating the burning of accumulated liver fat.
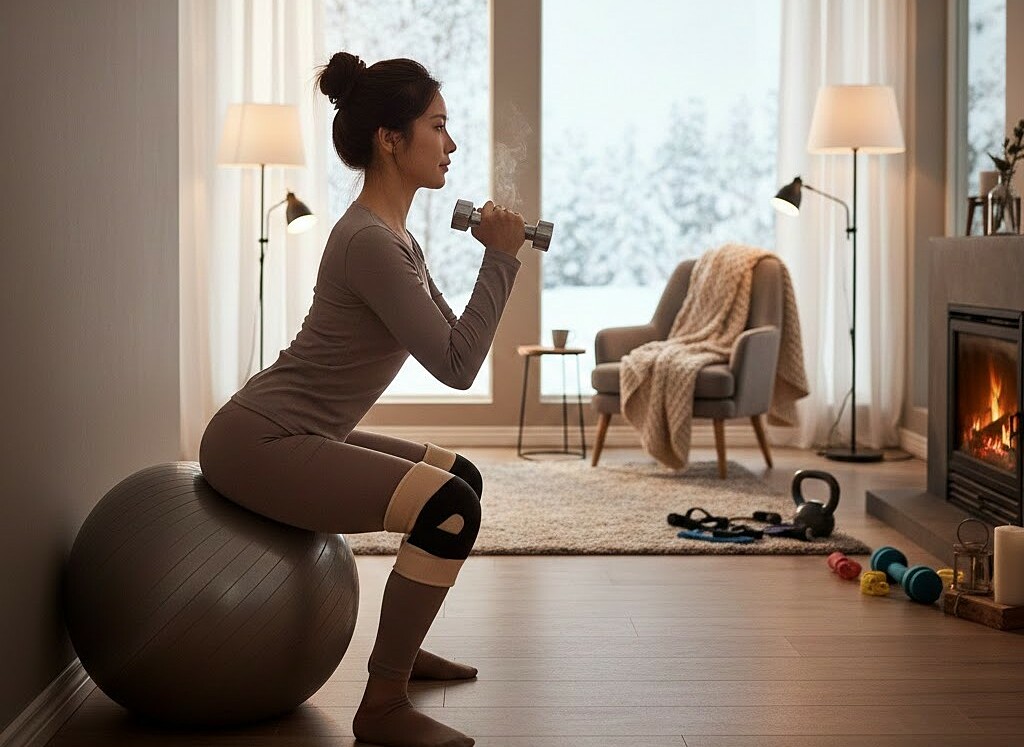 |
Exercise helps reduce liver fat. Photo created by AI |
Patients can aim for moderate aerobic activity, exercising three to five times a week for 30 minutes per session. This could involve brisk walking for 30 minutes or a slower walk for 40 minutes daily. Increasing routine activities such as house cleaning, cooking, laundry, and gardening also aids weight loss, reduces liver fat, and burns calories.
Once comfortable with aerobic exercises, incorporate resistance training two days a week. These workouts can utilize body weight, free weights, or resistance bands to enhance weight loss effectiveness.
Adopt dietary changes
A healthy diet benefits the liver and overall health. Patients should prioritize plant-based proteins like nuts, beans, and legumes. Incorporate healthy fats from extra virgin olive oil and avocados. Fatty fish such as salmon and sardines, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, help reduce inflammation.
Women should limit added sugar intake to no more than 24 g daily (six teaspoons). Men should not consume over 36 g daily (nine teaspoons). High sugar consumption contributes to fat accumulation in the liver and increased inflammation.
For each meal, dedicate one-half of the plate to non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter to whole grains such as brown rice, and the remaining portion to lean protein (tofu, fish, beans, chicken). Restrict fast food, fried dishes, and processed meats, as they can elevate liver fat and exacerbate inflammation.
The liver is responsible for metabolism and detoxification, including alcohol. Feelings of lightheadedness or intoxication signal that the liver is processing more alcohol than it can handle. Consequently, reducing alcohol intake supports liver cleansing.
Ensure adequate sleep
Insufficient sleep elevates the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and other serious health issues, including stroke, heart attack, and diabetes. Individuals with fatty liver should adopt healthy sleep habits: maintain a consistent sleep schedule, ensure a quiet and cool bedroom, limit electronic devices, and avoid high-intensity physical activity before bedtime.
By Anh Chi (Source: WebMD)
| Readers can ask questions about digestive diseases here for doctors to answer |