Answer:
Gallstones primarily form due to calcium crystal deposits within the pancreas. Chronic pancreatitis causes inflammation, damage, and calcification of pancreatic tissues, gradually leading to calcium deposits and the formation of stones in the pancreatic ducts or parenchyma. The common bile duct and pancreatic duct are located near and merge with each other. Stones in the distal common bile duct, especially those measuring 3-5 mm, can easily migrate into the pancreatic duct, causing pancreatic fluid blockage and gallstone formation.
Long-term excessive alcohol consumption also damages pancreatic tissue, hindering calcium absorption and leading to calcium accumulation and stone formation. Elevated blood calcium levels due to hyperparathyroidism or a prolonged high-calcium diet can also cause deposits in the pancreas, forming stones.
 |
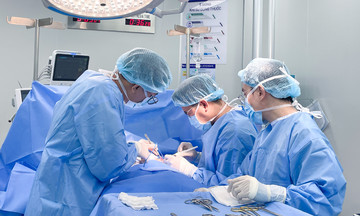
Doctor Le Khoa consults with a patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Other factors that increase the risk of gallstones include obesity, lack of exercise, smoking, high triglycerides, pancreatic duct stricture, or conditions like autoimmune disorders and cystic fibrosis. Gallstones often present no noticeable symptoms initially. Symptoms such as epigastric pain (above the navel), nausea, vomiting, and sometimes fever typically appear when stones become large and cause blockage.
The development of gallstones obstructs the flow of digestive enzymes from the pancreas to the small intestine, affecting the digestive system and leading to dangerous complications such as recurrent acute pancreatitis, infections, and multiple organ failure in severe cases. Typically, mild, asymptomatic gallstones require only conservative treatment. When the condition progresses and medical treatments are ineffective, surgery may be necessary. Depending on the individual case, the surgeon will determine the appropriate surgical approach, such as pancreatic duct drainage, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for stone removal, open surgery to remove stones and connect the pancreatic duct to the small intestine, or partial or total pancreatectomy. Early detection often allows for less invasive stone removal procedures with lower risks.
All surgical procedures carry potential risks and complications. It is advisable to take your grandfather to a hospital with comprehensive medical equipment and facilities, as well as experienced doctors, for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and reduced risk of complications.
MSc, MD, Specialist Level I Le Khoa
Center for Endoscopy and Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgery
Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City
| Readers can submit questions about digestive diseases here for doctor's answers. |