Doctor Nong Tuyet Phuong, from the Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology at Tam Anh Hanoi General Hospital, states that hormonal changes, increased nervous system sensitivity, and vehicle odors elevate the risk of motion sickness in pregnant women. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, nausea or vomiting, excessive sweating, fatigue, discomfort, and loss of appetite. In some cases, severe vomiting can lead to dehydration and low blood pressure, causing exhaustion. Here are some simple methods to reduce motion sickness for expectant mothers.
Get enough sleep
Pregnant women should avoid staying up late the night before their trip. Lack of sleep can lead to fatigue, reducing the body's ability to adapt to movement, which in turn increases nausea and motion sickness. Stress and anxiety can also worsen morning sickness and motion sickness symptoms.
Prepare thoroughly before the trip
Pregnant women should break long journeys into shorter segments to allow for rest stops, avoiding continuous travel for over 4 hours. Choosing an appropriate departure time, away from peak hours, can help reduce traffic congestion, fatigue, and nausea.
Eat light before departure
Pregnant women should neither travel on an empty stomach nor eat excessively before boarding a vehicle. Eating too much can cause bloating and heartburn, while hunger can lead to stomach discomfort, intensifying feelings of nausea. Meals before a trip should be light and easily digestible, such as bread, thin porridge, soup, or warm milk. Expectant mothers should avoid sour, spicy, oily, overly sweet, or strong-smelling foods.
Stay hydrated
Pregnant women should consistently drink plain water or fruit juice throughout their journey to prevent dehydration and uterine contractions. This also stimulates the digestive system, maintains adequate amniotic fluid levels, and ensures nutrient circulation to the fetus. Drink in small sips, avoiding large quantities at once.
In cases of severe vomiting and difficulty eating or drinking, expectant mothers must prioritize rehydration and electrolyte replenishment with plain water, correctly prepared oresol solution, or diluted ginger water to mitigate the risk of dehydration. If symptoms like excessive thirst, infrequent urination, dark urine, extreme fatigue, or dizziness when changing positions occur, pregnant women should seek medical attention.
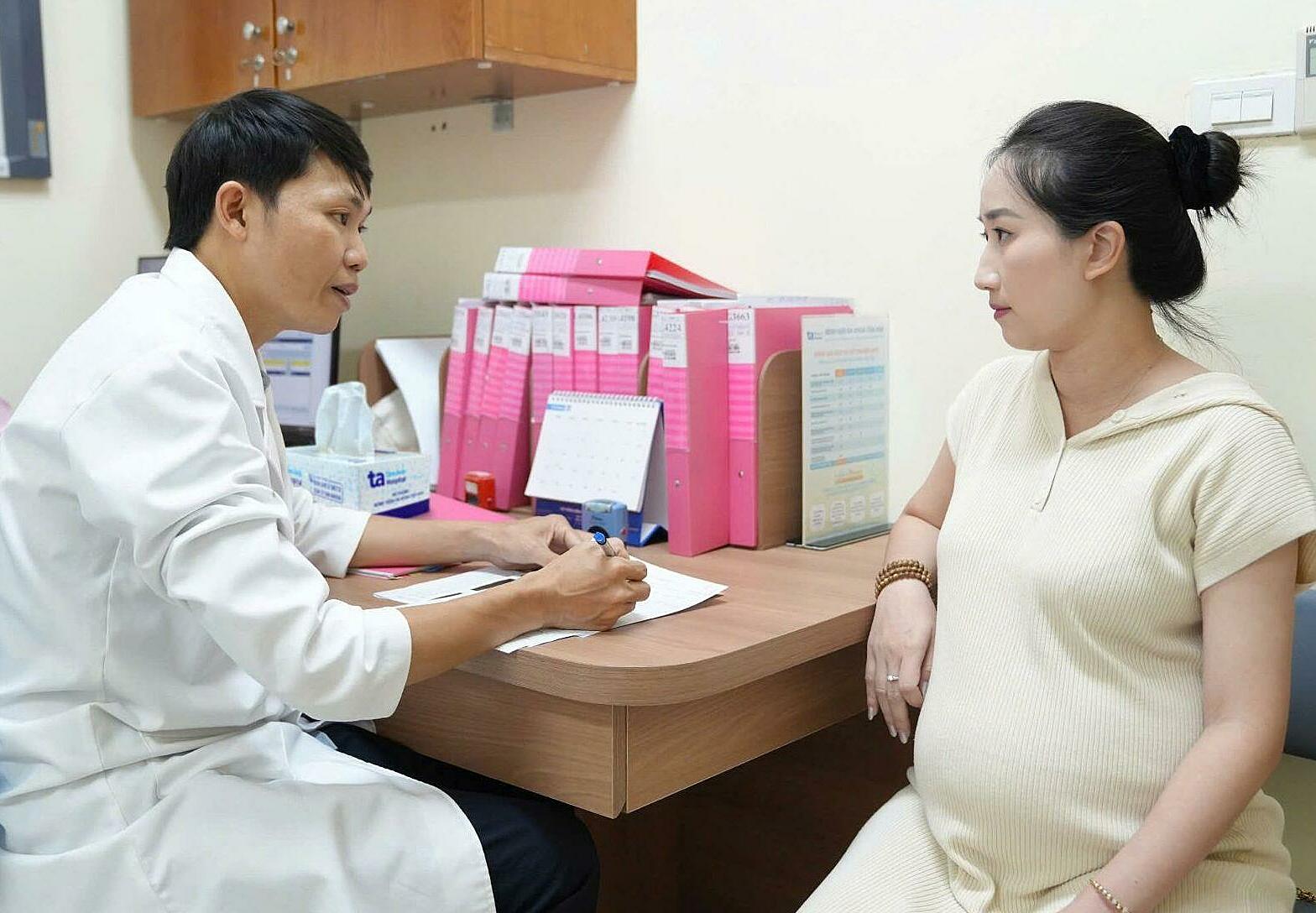 |
A doctor from the Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology consults a pregnant woman. Photo: Tam Anh Hanoi General Hospital |
Choose a suitable seating position
In cars or buses, pregnant women should select a seat with minimal vibration, such as the front seats near the driver or seats in the middle of the vehicle. When traveling by train, choose a middle carriage, and a seat or bed facing forward. On boats, a central seating position helps reduce swaying, and sitting near a window to look outside is preferable. On planes, seats over the wings or at the front are generally more stable, with less vibration and noise.
Limit triggers for the vestibular system
Pregnant women should avoid reading, looking at phones, or watching rapidly moving objects. Looking straight ahead in the direction of travel, closing eyes to rest, or conversing with family members can alleviate discomfort.
Wear a face mask
Fresh air significantly helps reduce motion sickness. Wearing a face mask throughout the journey helps minimize exposure to unpleasant odors and irritating exhaust fumes, thereby reducing nausea. Expectant mothers should open windows for air circulation or adjust the air conditioning to lessen feelings of stuffiness.
Chew gum or snack
Chewing helps reduce conflicting signals sent to the brain, which in turn alleviates discomfort. Pregnant women can chew gum or consume light snacks such as potato chips, fruit, or toast.
Use ginger, citrus peels, peppermint, or cinnamon essential oils
Inhaling natural aromas from citrus peels or essential oils can mask vehicle odors and soothe nausea and discomfort. Sucking on a fresh ginger slice, drinking warm ginger tea, or chewing ginger candy helps calm the stomach, reduce dizziness, and alleviate queasiness.
Breathe deeply, slowly, and evenly
Deep breathing stabilizes respiration, calms the nervous system, and reduces feelings of nausea and dizziness. If the body shows signs of fatigue, pregnant women should not continue traveling but should stop and rest.
Doctor Phuong advises pregnant women against self-medicating with anti-motion sickness drugs, especially during the first three months. In cases of severe motion sickness and excessive vomiting, medical advice should be sought for safe anti-nausea medication. When pregnant women travel long distances during Tet, families should research healthcare facilities along the route and prepare complete maternity records and contact information for the obstetrician in case of an emergency. After the trip, expectant mothers should rest adequately, eat light meals, and avoid strenuous activity. If a pregnant woman experiences prolonged nausea, dizziness for several hours, abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, or fever, she should go to the hospital immediately.
Trinh Mai
| Readers can submit questions about obstetrics and gynecology here for doctors to answer |