Long-distance driving demands continuous eye adjustment, often resulting in strain, fatigue, dryness, and slower reflexes. Doctor of first-degree specialization Nguyen Duc Huy, from the High-Tech Ophthalmology Department at Tam Anh General Clinic District 7, offers simple strategies to combat eye strain.
Take regular eye breaks
After every one to two hours of driving, drivers should stop for 5-10 minutes. Closing their eyes or gazing into the distance allows eye muscles to relax, restoring flexibility and easing retinal pressure. This habit not only prevents eye fatigue but also enhances concentration, reducing accident risks from delayed reflexes.
Blink frequently
Frequent blinking is a simple method to maintain natural eye moisture and alleviate pressure on the orbicularis oculi muscle and retina. It helps distribute the tear film evenly, clearing dust and impurities, thereby reducing the risk of keratitis or eye irritation.
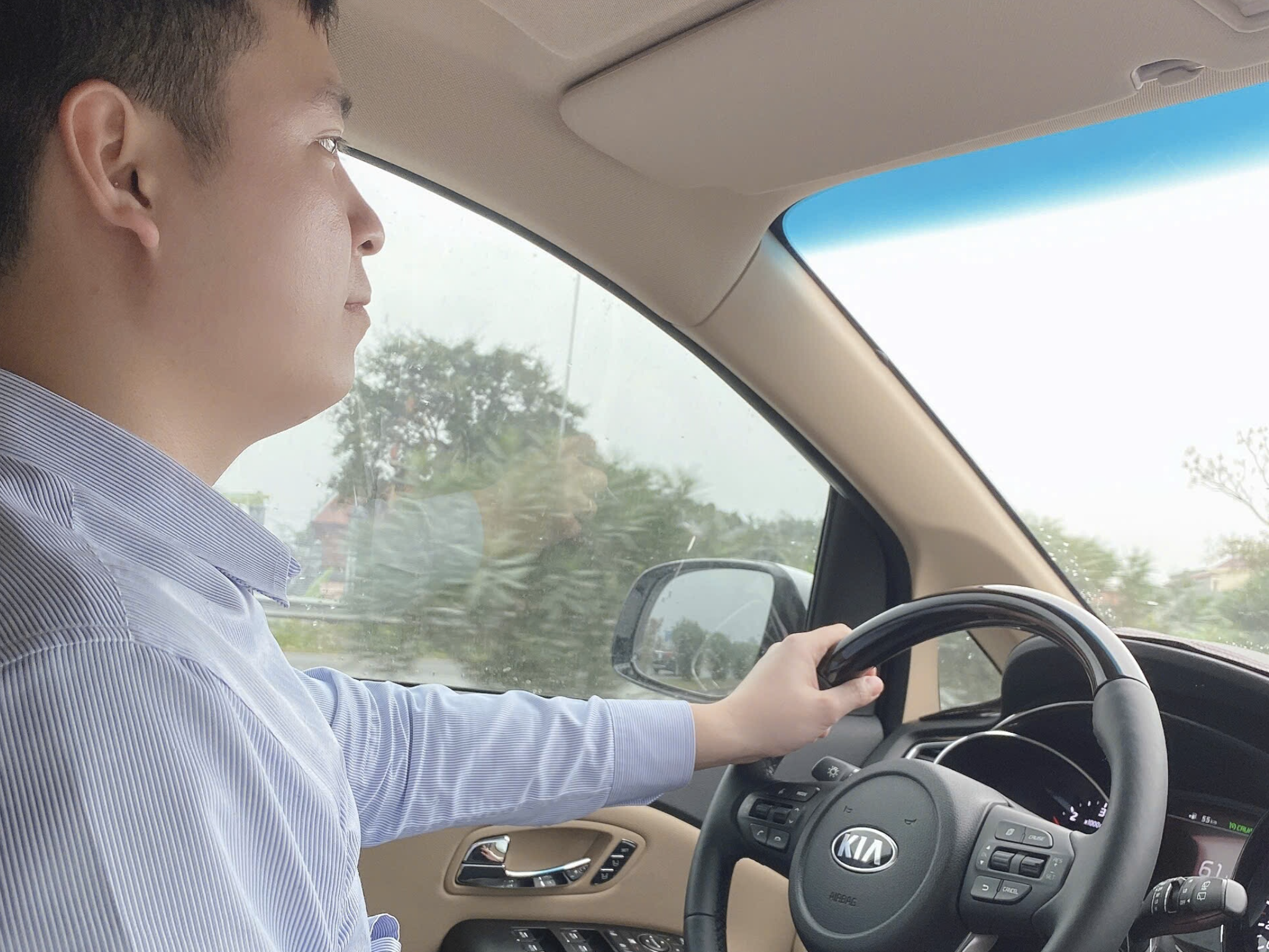 |
Long-distance driving demands high concentration, causing continuous eye adjustment and fatigue. Photo: Thanh Hoa
Adjust lighting appropriately
During long drives, eyes constantly adapt to varying light conditions—intense daytime sun, oncoming headlights, or dim night light—which can easily lead to eye strain, pain, and reduced concentration.
Adjusting lighting appropriately is a crucial step to alleviate eye pressure. During the day, drivers can wear anti-glare sunglasses to prevent excessive eye strain from direct sunlight. At night, avoid looking directly into oncoming headlights and adjust rearview mirrors to reduce glare.
Maintain proper hydration and nutrition
Eyes are prone to dryness from extended exposure to cold air conditioning inside the vehicle. Maintaining proper eye moisture can prevent strain, dryness, and reduce the risk of corneal irritation. Adequate hydration and nutritional support enhance eye flexibility, lessen muscle tension, and sustain high concentration throughout the drive.
Doctor Huy advises drivers to drink sufficient water, avoid smoking in the car, and use eye drops as needed to hydrate the cornea. Furthermore, consuming foods rich in omega-3, lutein, and vitamins A and C – such as fish, eggs, green vegetables, and carrots – can boost retinal resilience, enhance antioxidant defense, and protect eyes from blue light.
Nhat Minh
| Readers can send questions about ophthalmic diseases here for doctors to answer. |