According to Article 2 of the Law on Drug Prevention and Control, narcotic substances are addictive and psychotropic substances listed in the government's official drug catalog.
Decree 57/2022, amended by Decree 90/2024, categorizes narcotics into three lists: substances absolutely prohibited for medical and social use; substances with restricted use; and substances permitted in specific fields as regulated by competent authorities.
The Criminal Code uses these classifications and corresponding quantities to determine penalties for crimes such as illegal drug production, possession, transportation, and trafficking.
 |
Defendants in a drug case sentenced to a total of 11 death penalties by the Hanoi People's Court, 2/7. Photo: Danh Lam |
Defendants in a drug case sentenced to a total of 11 death penalties by the Hanoi People's Court, 2/7. Photo: Danh Lam
These crimes typically involve seven drug categories:
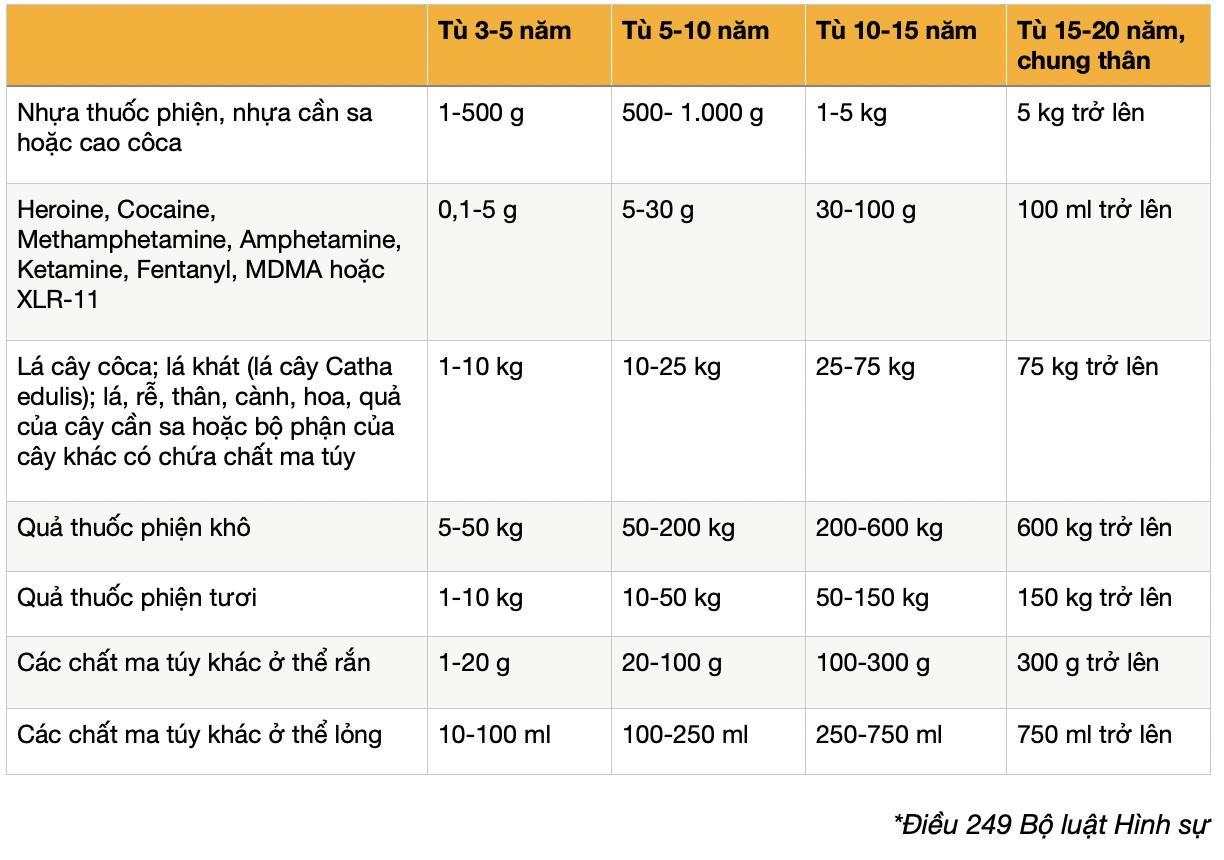
1. Opium resin, cannabis resin, or coca paste
2. Heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine, amphetamine, ketamine, fentanyl, MDMA, or XLR-11
3. Coca leaves; khat leaves (Catha edulis); leaves, roots, stems, branches, flowers, and fruits of cannabis plants or parts of other plants containing government-specified narcotics
4. Dried opium pods
5. Fresh opium pods
6. Other solid narcotics
7. Other liquid narcotics
Penalties for crimes involving category 2 drugs are more severe than others due to their highly addictive nature, life-threatening risks, and significant social impact.
For instance, possessing as little as 0.1 grams of a category 2 drug (heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine, etc.) is enough for prosecution and a minimum prison sentence of 3-5 years. Possessing 100 grams can result in life imprisonment, the maximum penalty for this crime.
The same penalty applies to the other six categories but requires larger quantities.
 |
Comparison of penalties for different drugs under the MDS for illegal transport, import, or export. |
Similarly, category 2 drugs carry the harshest penalties and lowest threshold quantities for other drug-related offenses.
Article 251 of the Criminal Code stipulates that trafficking 3 kg of heroin or cocaine (category 2) can result in the death penalty. This threshold is 30 kg for category 1, 150 kg for category 3, 1.2 tons for category 4, 300 kg for category 5, 9 kg for category 6, and 22 liters for category 7.
Some other countries apply similar rules. In Singapore, under the Misuse of Drugs Act (MDS), trafficking 15 g of heroin is punishable by death; for cannabis, the threshold is over 500 g, significantly stricter than Vietnam's 3 kg for heroin and 150 kg for cannabis.
 |
Singapore's Central Narcotics Bureau estimates that 15 g of heroin (the threshold for the death penalty) is equivalent to 1,250 doses, enough to satisfy the addiction of about 180 users for a week.
As of 12/1/2025, Vietnam has over 249,000 individuals either using illegal drugs, addicted to drugs, or under post-rehabilitation management. There are 989 reported cases of methamphetamine-induced psychosis nationwide.
In 2024, 25,951 drug users and addicts committed legal violations, including 8,119 administrative violations and 17,832 criminal offenses.
2024 also saw 36 cases of social disorder caused by 36 individuals experiencing methamphetamine-induced psychosis. These incidents included five murders, seven cases of intentional injury, and other offenses like resisting arrest, property damage, public disorder, and unlawful detention.
Drug use among drivers, especially truck, bus, and taxi drivers, continues to rise: 5,175 drivers tested positive for drugs, a 76.3% increase (2,240 cases) compared to 2023.
Ministry of Public Security - Drug Prevention and Control Report 2024
Hai Thu












