Not all exercises burn the same amount of calories. Activities like running or high-intensity interval training (HIIT) require the body to work harder and expend more energy. The number of calories burned also depends on factors like age, weight, and individual training frequency.
Weightlifting increases muscle mass, which helps the body burn more calories. A 30-minute weightlifting session can burn approximately 216 calories for a person weighing around 68 kg. Incorporating strength training alongside cardio can also boost calorie expenditure.
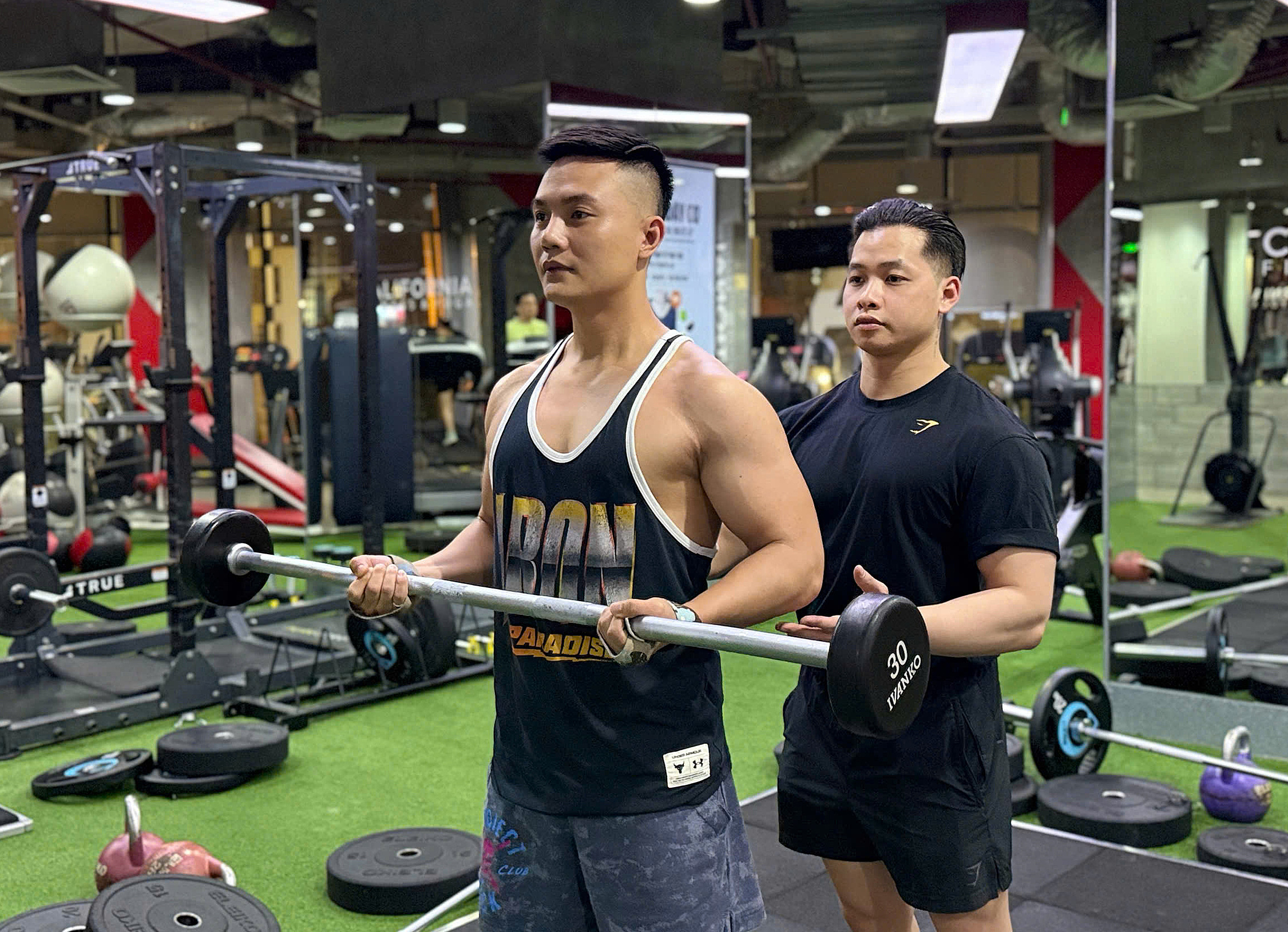 |
Weightlifting increases muscle mass, which helps the body burn more calories. Illustration: Chu Tran |
Jumping rope engages the upper body, lower body, and core muscles. Not only does it improve cardiovascular health and support weight management, but jumping rope can also burn over 260 calories in a 30-minute session, more than activities like walking, swimming, cycling, and tennis.
HIIT involves alternating short bursts of high-intensity exercise with periods of lower intensity or brief recovery. HIIT offers numerous benefits, including weight loss, improved fitness, and better cardiovascular health.
Due to how the body uses oxygen during recovery after exercise, HIIT workouts can burn 15% more calories than traditional, steady-state workouts. Additionally, HIIT is quick and delivers fast results, potentially burning upwards of 350 calories in a half-hour session.
Cycling typically burns more calories than other activities, depending on speed, incline, and whether it's stationary or outdoors. A person weighing around 70 kg cycling at least 16 km/h can burn approximately 295 calories in 30 minutes.
Hiking combines aerobic activity and strength training due to the use of various muscle groups. It's estimated that a person weighing around 68 kg can burn about 210 calories during a 30-minute hike. This activity can also improve mood, reduce stress, and boost the immune system.
Tennis benefits both physical and mental health, reducing the risk of heart disease, obesity, and depression. Playing singles tennis for 30 minutes can burn around 200 calories for a person weighing around 68 kg. Doubles tennis is also a moderately intense activity safe for daily play.
Swimming is a low-impact but highly effective exercise for individuals recovering from injuries or those seeking to improve muscle control in conditions like Parkinson's disease and other movement disorders. As it involves muscle and cardiovascular activity, swimming freestyle at a relatively slow pace can burn approximately 255 calories in a 30-minute session.
Running is a high-intensity activity that burns approximately 300 calories in 30 minutes at a pace of 8 km/h. Increasing the speed to a 10 km/h sprint can burn over 600 calories in the same timeframe. Running has many health benefits, including strengthening muscles, increasing bone density, improving cardiovascular health, and preventing chronic diseases.
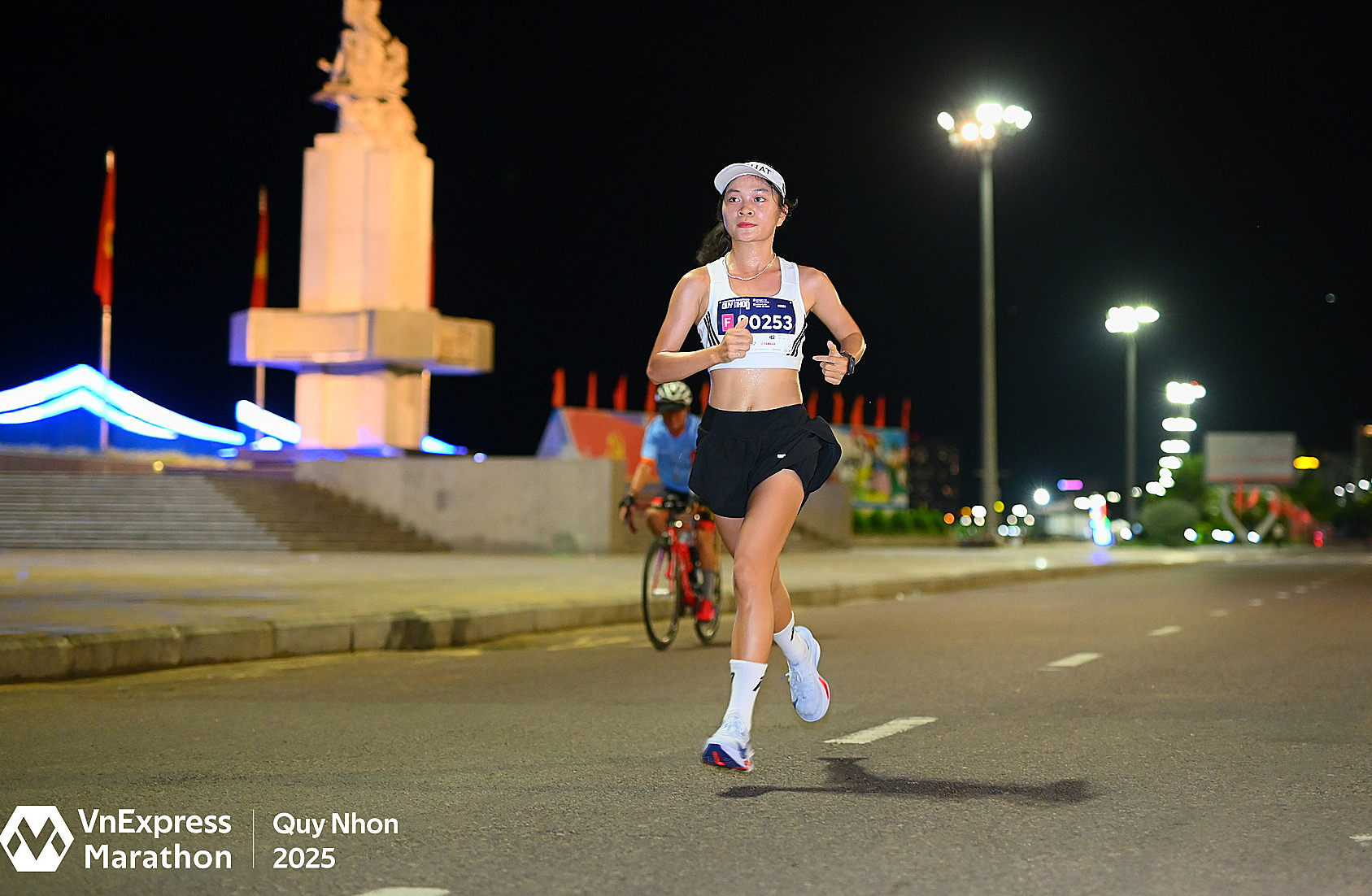 |
Running has many health benefits. Photo: VM |
Stair climbing is considered a physical activity and can burn extra calories, especially when carrying weights. It can increase calorie expenditure by 8 to 10 times the amount burned at rest. A 30-minute stair-climbing session burns approximately 280 calories for a person weighing 70 kg.
Dancing can burn around 165 calories in a 30-minute session, although the exact number varies depending on the specific style. Research suggests that dancing supports muscle, heart, and bone health by reducing fat, blood pressure, and LDL (bad cholesterol) levels.
Factors influencing calorie expenditure include:
: Age: Muscle mass naturally decreases with age, potentially slowing down an individual's calorie-burning rate.
: Weight: Heavier individuals expend more energy during physical activity compared to those with average or lower weights, thus burning more calories when exercising at a comparable level.
: Muscle mass: As muscle burns more calories than fat, individuals with more muscle mass tend to burn more calories.
: Gender: Men generally burn more calories than women during the same exercise, possibly due to physiological factors.
: Duration, intensity, and type of exercise: The timeframe and intensity of different physical activities result in varying calorie expenditure.
Some ways to burn more calories during exercise include:
: Adding weights to activities to build muscle and increase calorie burn.
: Moving quickly and continuously to maintain calorie expenditure.
: Increasing steps during workouts, such as parking farther from the gym entrance or walking around the tennis court before a match.
: Wearing a smartwatch to track workouts, daily steps, and other health indicators.
Small lifestyle changes can also help burn more calories throughout the day: standing instead of sitting while taking phone calls or reading work emails; opting for stairs instead of elevators; doing household chores like vacuuming and gardening; and limiting screen time. Taking breaks and stretching regularly while sitting at work can also contribute.
Consult a doctor before starting a new exercise routine if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or injuries.
Anh Ngoc (According to Verywell Health)
| Readers can submit questions about musculoskeletal diseases here for doctor's answers. |