|
Gallstones often develop silently without causing symptoms. They can block the bile ducts connecting the gallbladder to the small intestine, causing severe abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. A healthy, nutrient-rich diet can reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
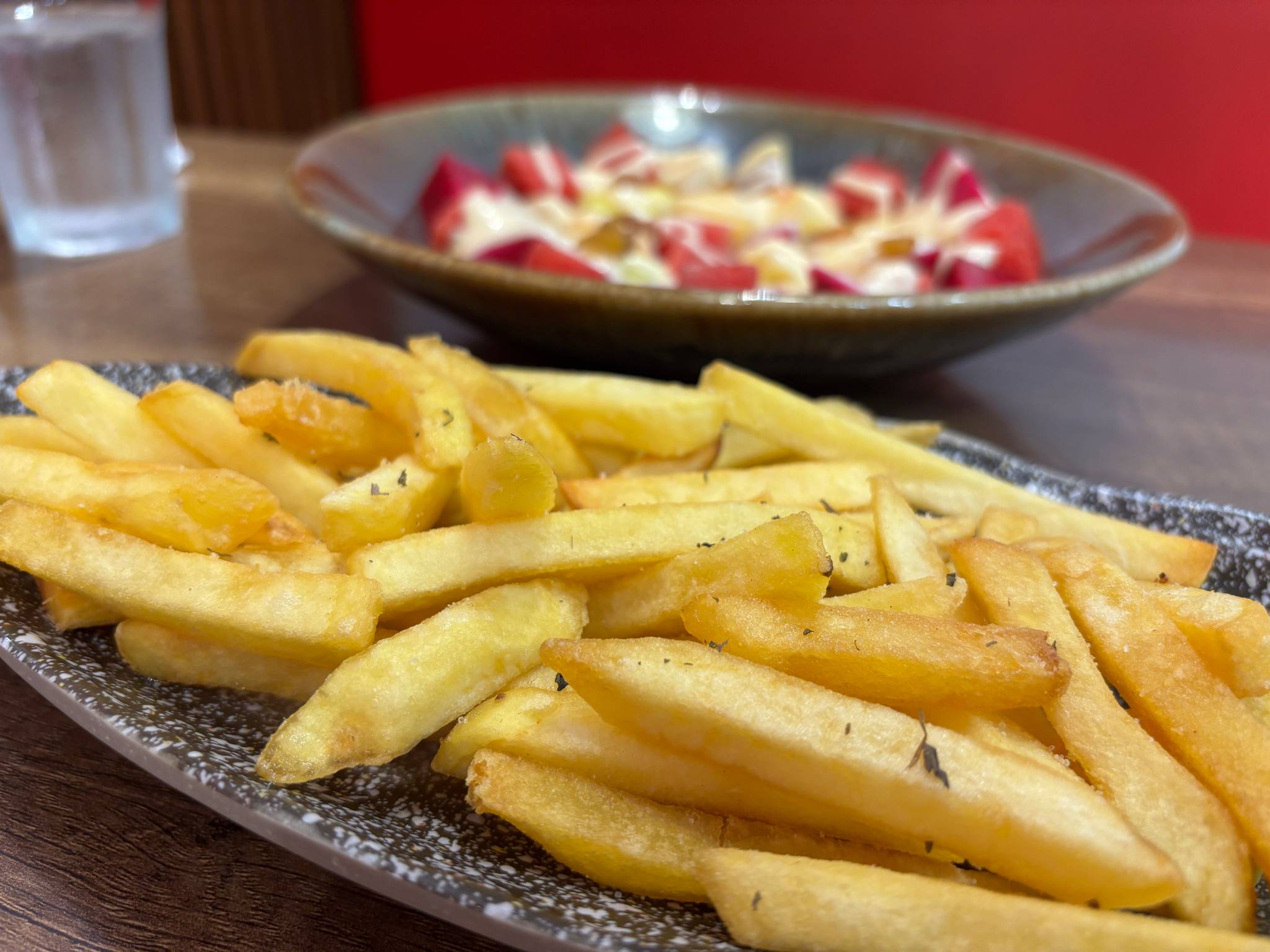
French fries are high in saturated and trans fats. The gallbladder releases bile to help the body digest fats. A high-fat diet can overload the gallbladder, leading to abdominal cramps. It's advisable to distribute fat intake moderately throughout the day, avoiding large, greasy meals. Deep-fried foods often lead to indigestion and bloating, which are not beneficial for the intestines.
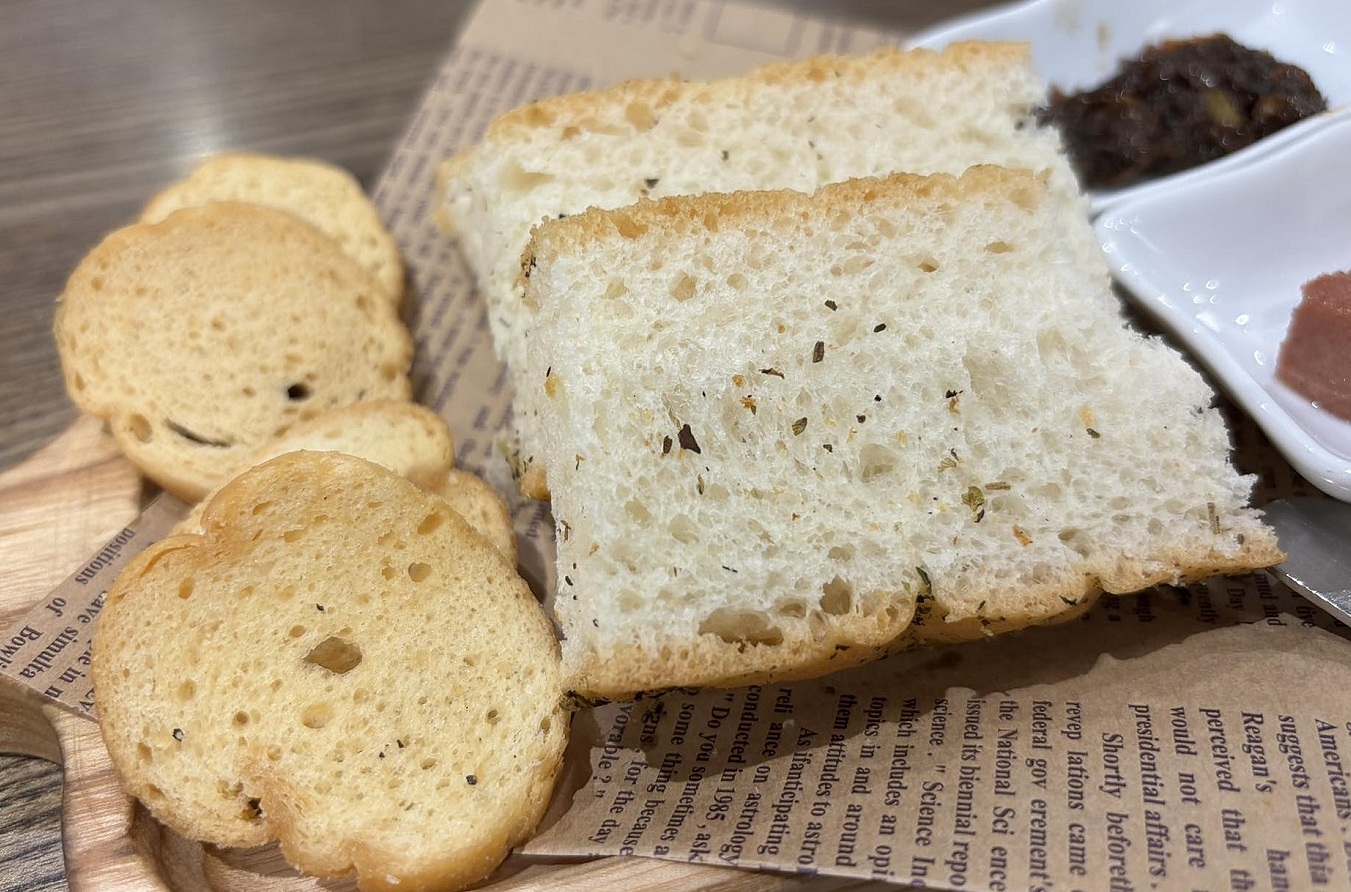 |
White bread, primarily composed of refined white flour, contains little to no fiber, increasing the risk of gallbladder problems. White bread and pasta are often high in refined carbohydrates that can raise blood sugar levels, stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin. This sudden change can affect bile production and secretion.
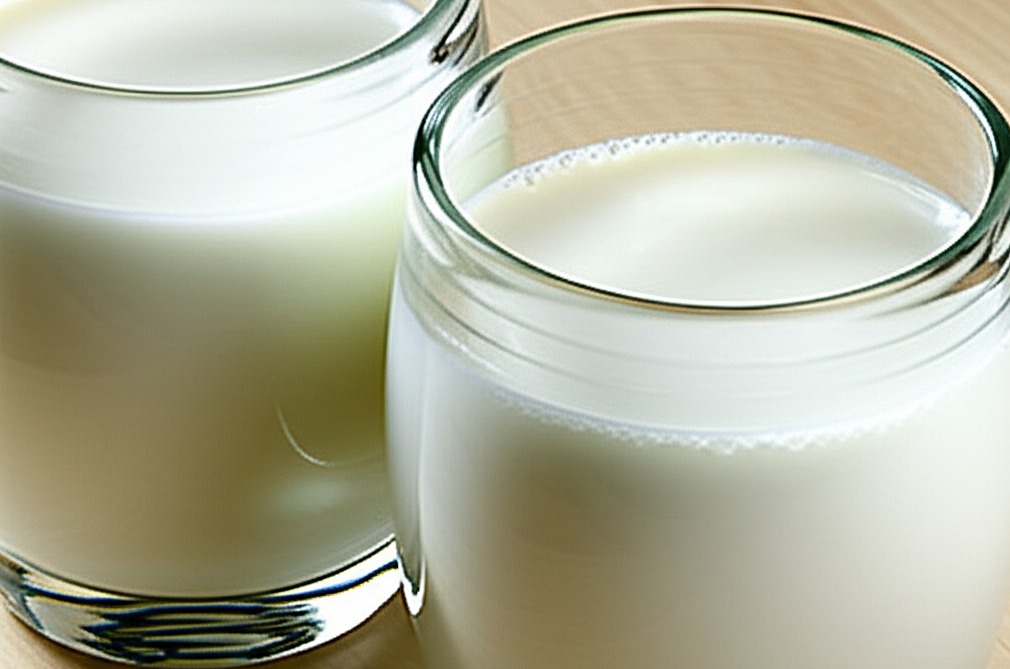 |
Whole milk is high in saturated fat, which slows digestion and increases the likelihood of cholesterol precipitation and gallstone formation. Consuming a lot of fat can force the gallbladder to contract more vigorously to digest it, increasing pressure on the gallbladder.
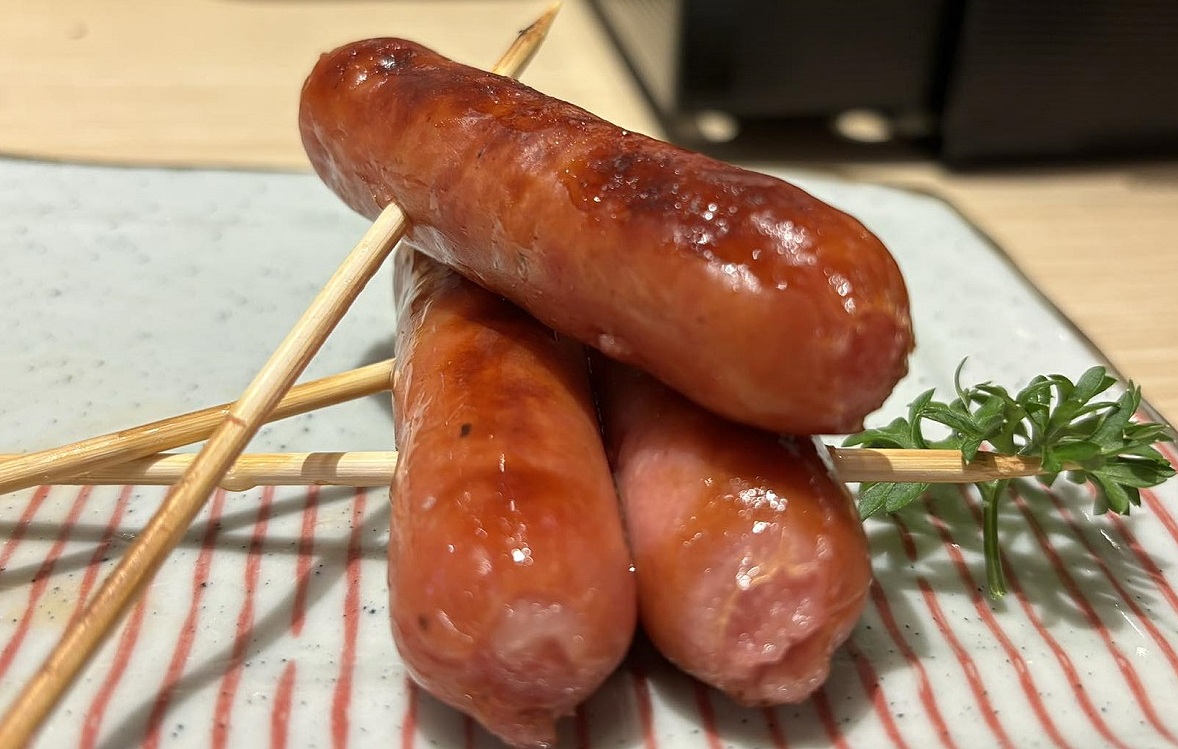 |
Processed meats, such as sausages and bacon, are high in saturated fat and cholesterol. Frequent consumption can increase cholesterol levels in bile, contributing to gallstone formation. They are also high in preservatives and food additives, which can irritate or damage the liver and gallbladder, affecting bile production and secretion.
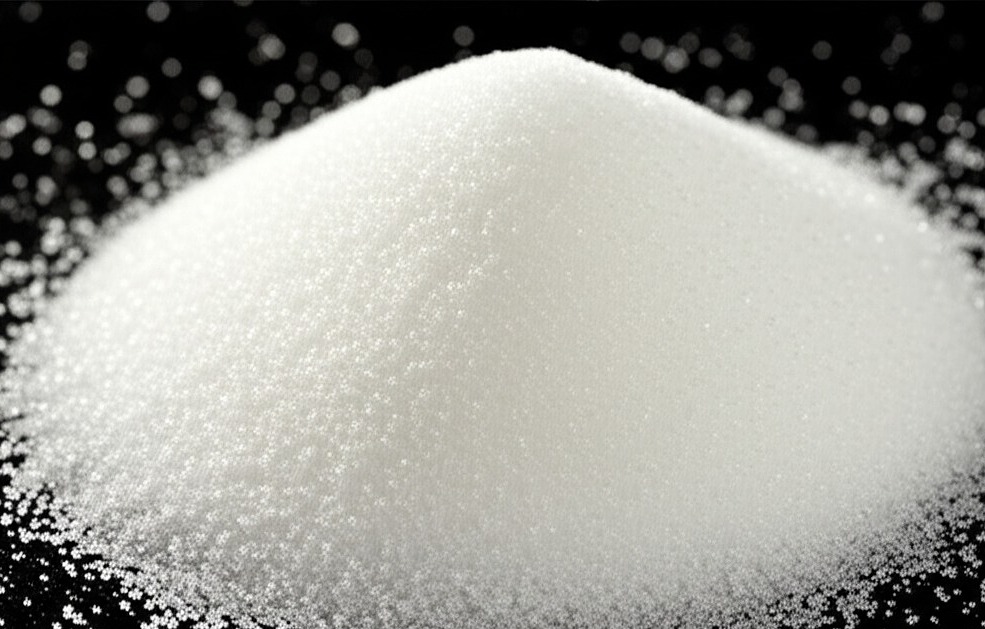 |
Sugar negatively affects blood sugar levels and is linked to an increased risk of gallstones. Excessive sugar intake can cause problems related to bile balance and fat metabolism, which are harmful to the gallbladder. Examples of high-sugar foods include soft drinks, energy drinks, candy, and pastries.
Anh Chi (According to Heathline, Very Well Health)
Images: Anh Chi, AI