Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory joint disease. It occurs when the immune system, which normally protects the body from bacteria or virus, malfunctions and attacks healthy tissues. This leads to inflammation of the synovial membrane, causing joints to become swollen, warm, red, and painful. If not well-controlled, RA can damage other organs throughout the body.
Currently, the exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis and a complete cure have not been found. However, early and proper treatment can help control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the patient's quality of life. Treatment methods for rheumatoid arthritis include:
Medical treatment primarily involves medication and physical therapy. Patients are prescribed pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce symptoms, along with DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) to control the disease and reduce inflammation. Physical therapy enhances pain reduction, improves mobility, strengthens muscles, and prevents joint stiffness and deformity, contributing significantly to a patient's functional capacity.
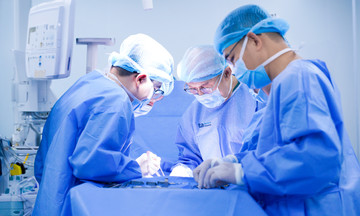
Surgery is indicated in cases of severe joint damage where conservative treatments are insufficient. Doctors replace the damaged joint with an artificial joint to restore mobility for the patient. Typically, knee and hip joints are the most common ones replaced due to their weight-bearing nature and frequent involvement in RA.
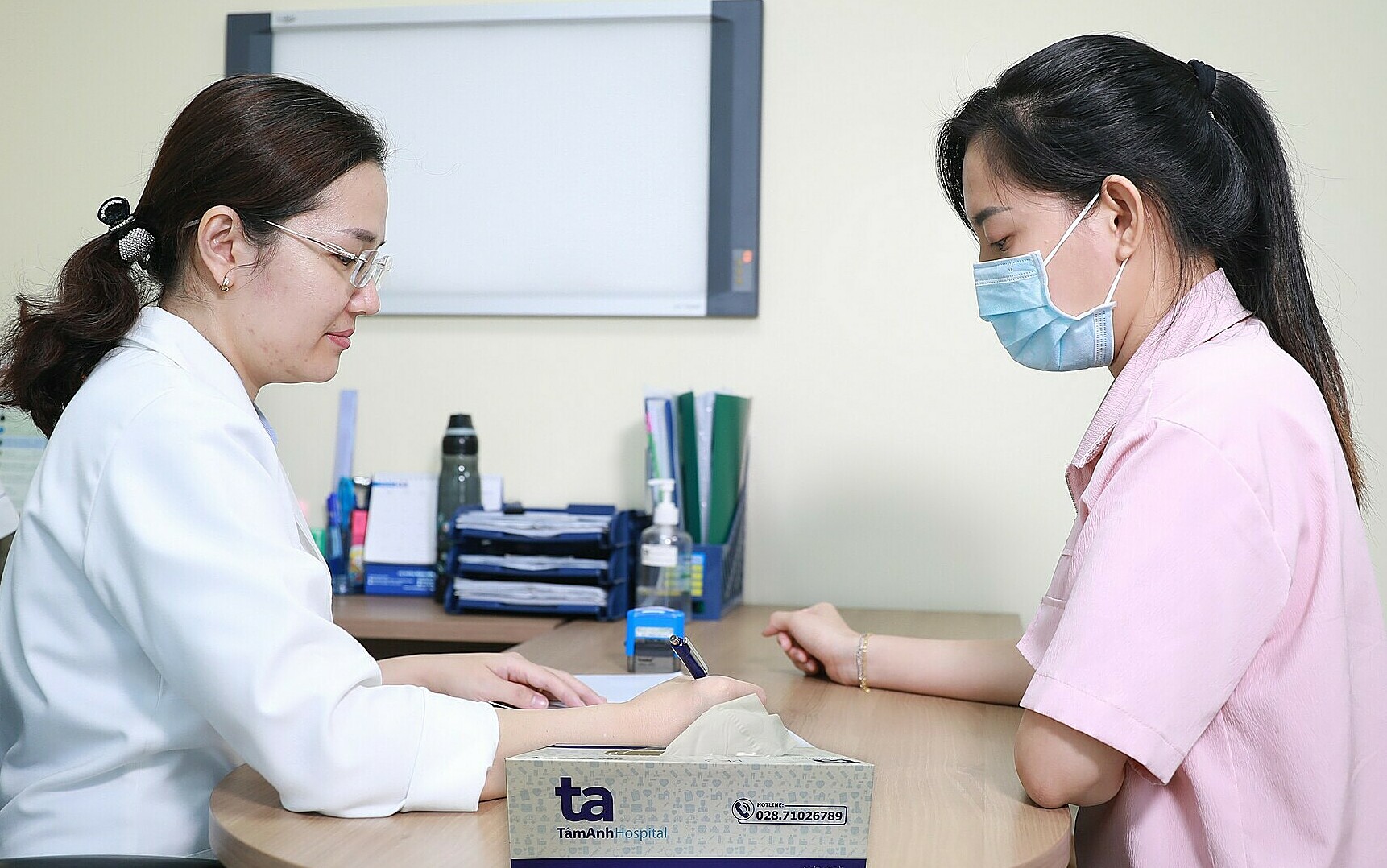 |
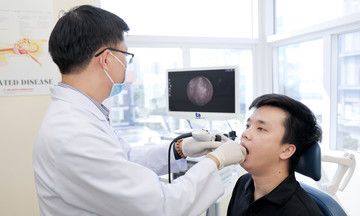
Doctor Thu explains test results to a patient. Illustration: Tam Anh General Clinic District 7 |
To enhance treatment effectiveness, you should combine medical interventions with a healthy lifestyle. This includes regular exercise at an appropriate intensity to keep joints flexible and supple. While no specific diet treats rheumatoid arthritis, some foods effectively reduce inflammation. You should consume plenty of whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and omega-3-rich foods such as tuna, salmon, mackerel, herring, chia seeds, and walnuts. Simultaneously, avoid excessive consumption of red meat, fast food, and highly salted or processed foods, which can exacerbate inflammation.
Uncontrolled rheumatoid arthritis not only affects all joints in the body and increases the risk of disability but can also damage other organs such as the eyes, lungs, and cardiovascular system. Once these complications occur, they are difficult to recover from, highlighting the importance of proactive management. If you have been diagnosed with the disease, you should adhere to your doctor's treatment instructions, undergo regular check-ups, or seek immediate attention if you notice any abnormalities.
Master, Doctor Pham Thi Xuan Thu
Musculoskeletal Internal Medicine Unit
Tam Anh General Clinic District 7
| Readers can send questions about musculoskeletal diseases here for doctors to answer. |