Response:
Influenza A is a contagious illness caused by a virus. It typically appears during seasonal changes and can spread rapidly within the community. Individuals infected with the influenza A virus often experience a high fever, cough, sore throat, fatigue, loss of appetite, and body aches.
Those with influenza A should not self-medicate with antibiotics unless specifically instructed by a doctor. Antibiotics are effective only against bacteria; they do not kill viruses. Misusing antibiotics risks causing drug resistance, making subsequent bacterial infections more challenging to treat. Over-reliance on antibiotics can also lead patients to neglect proper care measures.
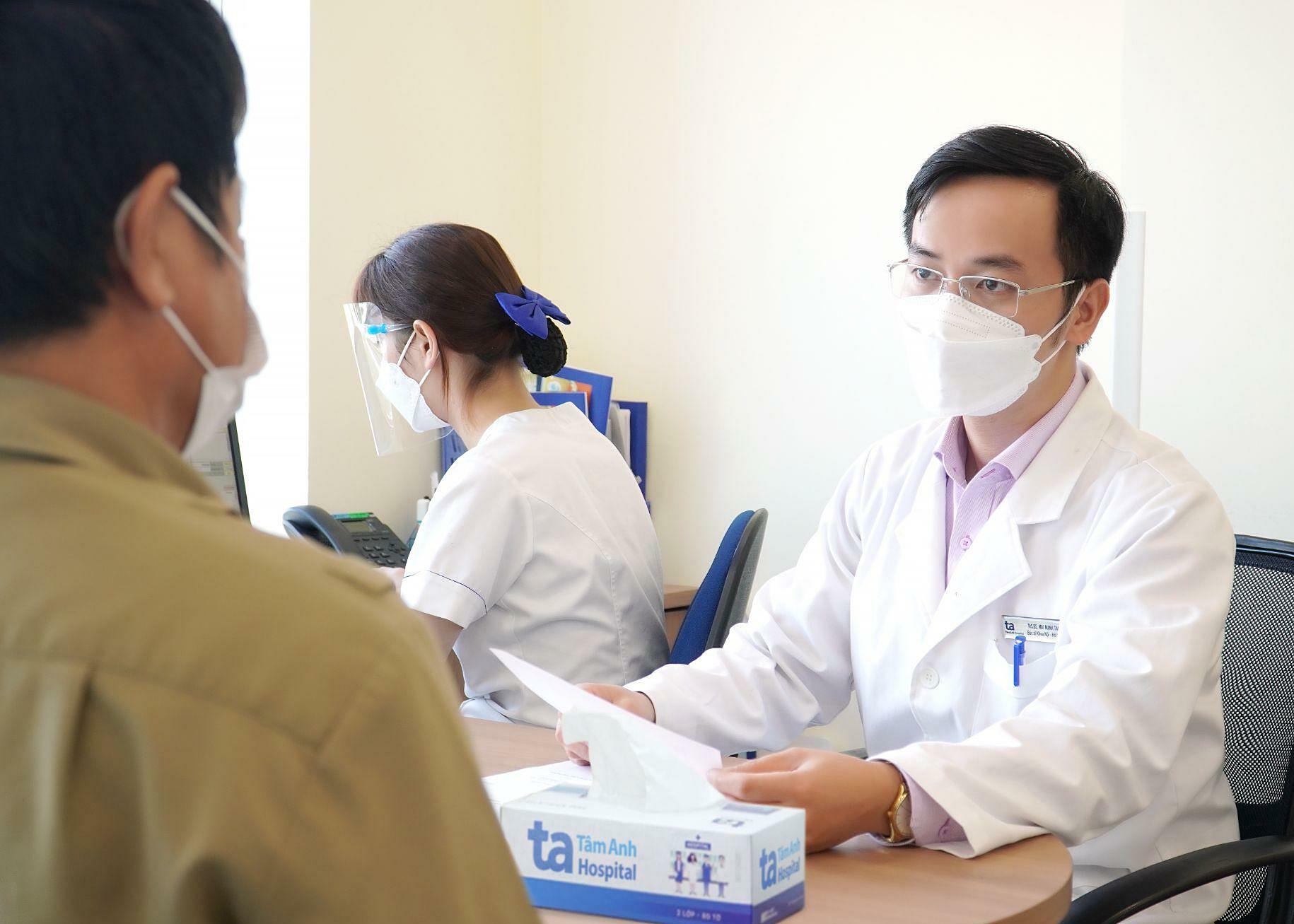 |
A doctor examines an influenza A patient. Illustration: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Treatment for influenza A primarily focuses on alleviating symptoms and supporting the body's recovery. Patients should rest and drink plenty of fluids to replenish hydration and thin respiratory secretions. For fever or body aches, individuals may use fever-reducing and pain-relieving medication. The diet should prioritize soft, easily digestible foods such as porridge and soup, supplemented with fruits and vegetables to boost immunity. Cleaning the nose and throat with physiological saline solution helps clear secretions, reduces nasal congestion, and improves breathing. In specific cases, a doctor might prescribe antiviral medication to shorten the illness duration and minimize the risk of complications.
Master, Doctor Dang Thanh Do
Respiratory Department
Tam Anh General Hospital Hanoi
| Readers can submit respiratory health questions here for doctor consultation. |