Boiled animal blood, an affordable food, offers various health benefits when consumed properly. However, moderation is key, as it contains a relatively high cholesterol content. While nutritious, caution is necessary, especially regarding preparation methods, to avoid potential health risks.
Boiled blood from animals like pigs, chickens, and ducks is a rich source of nutrients. For example, 100 g of pig blood contains 16 g of protein, exceeding that found in both beef and pork. The protein in pig blood includes amino acids similar to those in the human body, facilitating easy absorption and digestion. Additionally, pig blood provides lecithin, iron, and other essential elements vital for bodily functions.
In Traditional Eastern Medicine, boiled blood is known for its cooling properties and sweet taste. It is valued as a blood tonic, supporting blood circulation and enhancing the health of individuals experiencing weakness, dizziness, or blurred vision. This dish also offers detoxification capabilities, particularly pig and duck blood. It helps cleanse the intestines, eliminate toxins, and reduce 'internal heat' (a Traditional Eastern Medicine concept referring to an imbalance that can cause various symptoms). Furthermore, it aids in purifying the digestive system, absorbing accumulated toxins, and expelling them from the body.
Due to its high iron content, boiled blood helps replenish iron in the body, improving anemia and boosting red blood cell production. Traditional Eastern Medicine also suggests that boiled blood stabilizes blood pressure, improves respiratory function, and reduces cough symptoms. Moreover, the calcium present in boiled blood contributes to bone health, helping prevent bone-related issues such as osteoporosis. It serves as a natural calcium supplement, particularly beneficial for older adults and those needing to strengthen their bones. The dish is also believed to reduce stress, replenish energy, and restore mental well-being for individuals frequently experiencing fatigue or tension from work or studies.
Despite its benefits, consuming too much boiled blood is not advisable due to its relatively high cholesterol content. This is especially true for individuals at high risk of cardiovascular disease or elevated blood fat levels. When purchasing, choose fresh, bright red blood from recently slaughtered pigs or chickens. Ensure the vendor maintains clear hygiene standards to avoid unsafe products.
Individuals with weak digestive systems or those prone to diarrhea should limit their intake of boiled blood, as its cooling properties might further chill the body and lead to indigestion. Absolutely do not use blood for 'tiet canh' (raw blood pudding), as this dish is highly susceptible to bacterial contamination. Such contamination can potentially cause streptococcus suis infection or other forms of food poisoning.
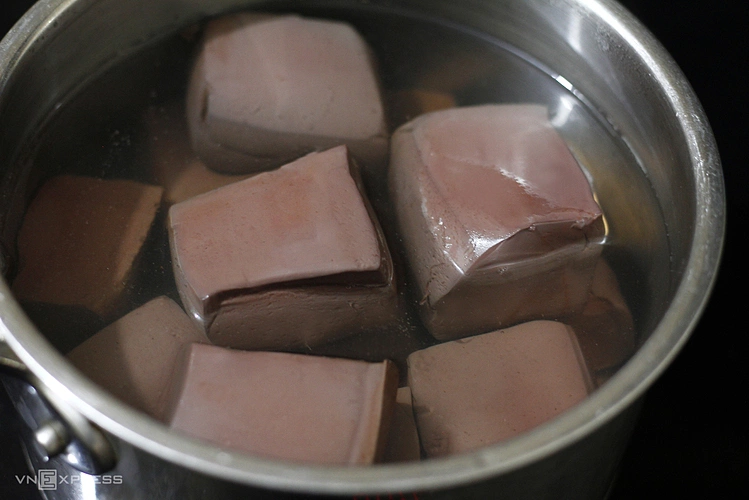 |
Boiled blood offers many benefits, but excessive consumption can negatively impact blood fat levels. Photo: Bui Thuy
Traditional Medicine Practitioner Do Minh Tuan
Hanoi Traditional Medicine Association