Master, Resident Doctor Nguyen Xuan Quang, Head of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery at Hong Ngoc General Hospital, stated that parotid gland tumors are uncommon in the head and neck region, accounting for about 4% of cases, yet they are highly complex. This is because the area contains a network of facial nerves, especially the facial nerve VII, which traverses the entire parotid gland and branches densely within the glandular tissue. Therefore, even minor damage during dissection can cause facial distortion, facial paralysis, and affect aesthetic function.
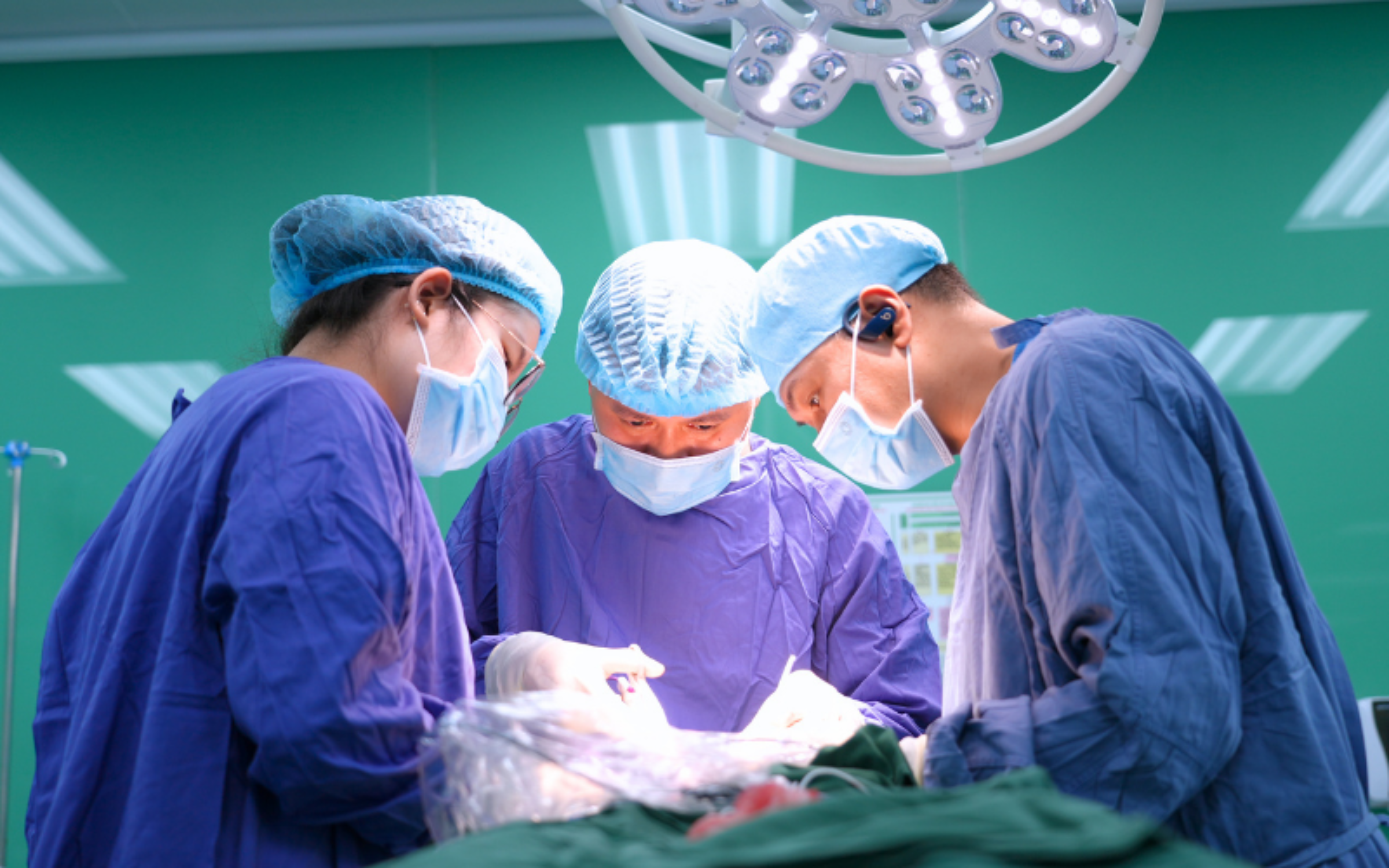 |
Surgery is the most effective treatment for parotid gland tumors. Photo: Hong Ngoc General Hospital |
Surgery is the most effective treatment for parotid gland tumors. Photo: Hong Ngoc General Hospital
Surgery is the most effective treatment for parotid gland tumors, aiming to remove the entire tumor while ensuring the safety of the facial nerve. This presents a significant challenge because the facial nerve VII runs deep, branches within the gland, and is almost completely encased. Thus, every maneuver must be absolutely precise to avoid damage that could lead to facial paralysis after surgery.
Previously, without a nerve monitor (NIM), surgeons had to locate and expose the entire facial nerve before excising the tumor, even for superficial masses. This method reduced the risk of nerve damage but often resulted in the removal of much healthy glandular tissue, leading to potential complications such as salivary fistula, Frey's syndrome, facial asymmetry, and still carried a risk of facial paralysis.
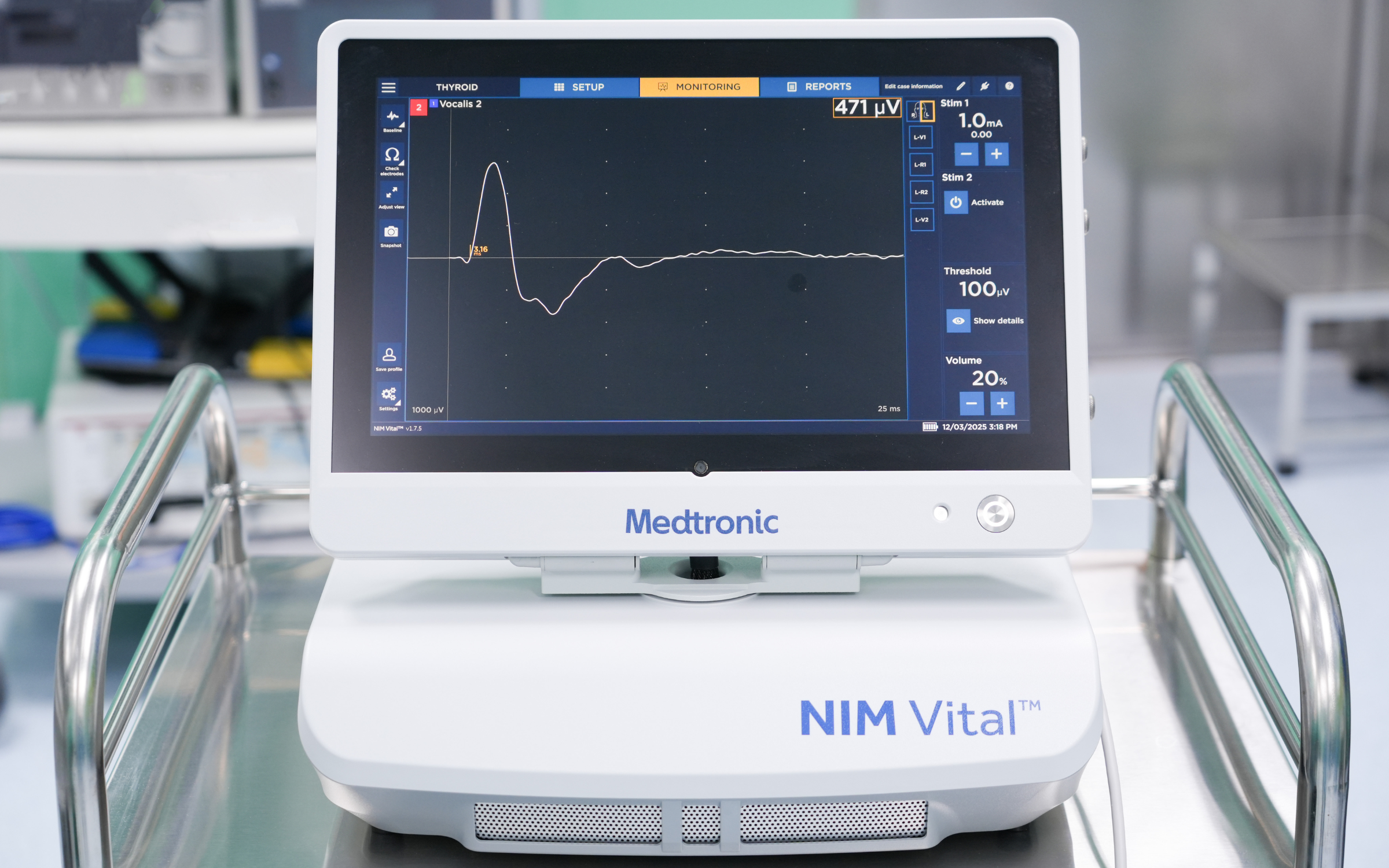 |
New generation nerve monitor (NIM). Photo: Hong Ngoc General Hospital |
New generation nerve monitor (NIM). Photo: Hong Ngoc General Hospital
Currently, with the application of NIM, the facial nerve is continuously monitored during surgery. The system provides alerts when the surgeon operates near or touches the nerve, enabling more precise and safer dissection.
Thanks to NIM, for tumors smaller than 3 cm, surgeons can directly access and dissect the tumor capsule without fully exposing the entire nerve. This approach minimizes the risk of facial nerve damage, while preserving most of the healthy glandular tissue and maintaining natural facial contours after surgery.
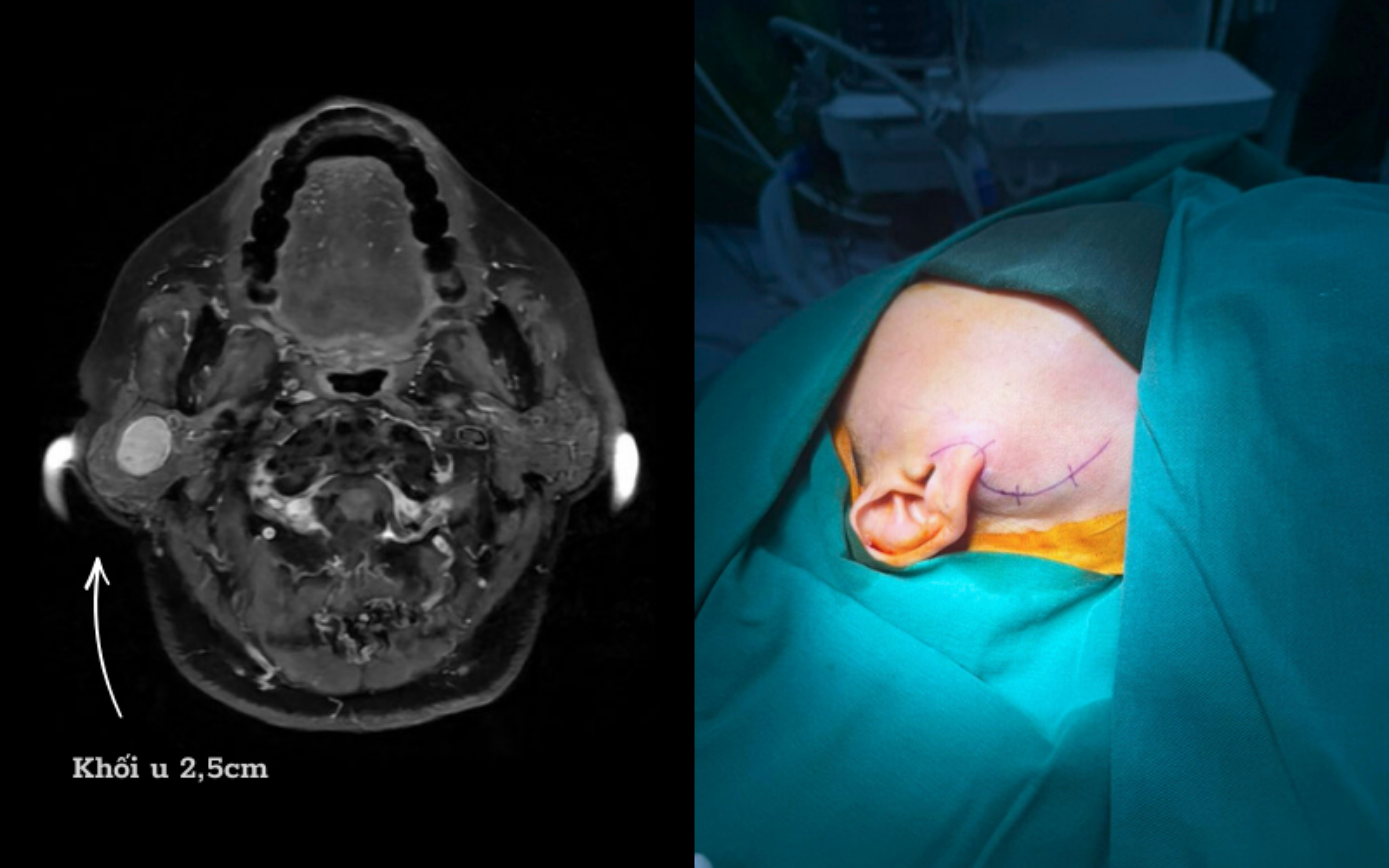 |
The patient's parotid gland tumor was in a complex position. Photo: Hong Ngoc General Hospital |
The patient's parotid gland tumor was in a complex position. Photo: Hong Ngoc General Hospital
The hospital has applied NIM in hundreds of cases, notably a female patient, 73 years old, who had a right parotid gland tumor for many years, presenting with swelling at the jaw angle and discomfort. Although early surgery was indicated, the patient delayed due to fear of facial paralysis, causing the tumor to grow larger, compress the nerve, and complicate the surgery. Faced with this situation, Doctor Quang and his team used a new generation nerve monitor (NIM) to safely dissect the tumor.
Patient D.'s surgery lasted 3 hours. The tumor was completely removed without requiring total parotidectomy. Post-surgery, the patient recovered quickly, experienced no facial nerve paralysis, and maintained facial symmetry and aesthetics.
Doctors recommend early treatment for parotid gland tumors. Surgery performed at a specialized facility equipped with modern nerve monitoring systems helps ensure patient safety, reduces complications, and maximally preserves facial function and aesthetics.
Van Ha