Calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease is also known as pseudogout. Both CPPD and gout are forms of arthritis, where small crystals form in joints and surrounding tissues leading to swelling, pain, and stiffness.
Monosodium urate (uric acid) crystals are the cause of gout. Uric acid is a waste product from the breakdown of purines, a substance found in the body and in food. Normally, the kidneys filter out excess uric acid. However, when this excretion process malfunctions, it leads to too much uric acid in the blood. This can accumulate and form needle-shaped crystals in the joints. These crystals rub against the synovium - the lining of the joint - leading to inflammation, pain, and swelling.
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals are commonly found in bones and teeth. In people with CPPD, these crystals form in the cartilage. CPPD crystals are rhomboid-shaped with blunt ends. In many cases, CPPD crystals do not cause any symptoms. However, when the crystals move from the cartilage into the joint cavity, they can rub against the soft tissue, causing pain and swelling.
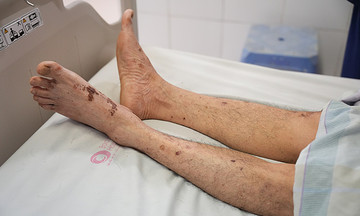
Gout usually only flares up in one joint at a time. The patient experiences severe pain, heat, swelling, and redness in the joint. The disease often occurs in the big toe, but can also affect other joints in the body including the ankles, elbows, shoulders, knees, and hips. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), symptoms can last from a few days to a few weeks.
CPPD has symptoms similar to gout, which can lead to severe pain and rapid joint stiffness, peaking within 12-24 hours. Other symptoms include joint swelling, fever, sweating, and fatigue. CPPD is most common in the knees, but can also occur in the wrists, shoulders, ankles, elbows, toes, and hips. The level of pain is usually milder than gout. Symptoms can last from a few days up to two weeks.
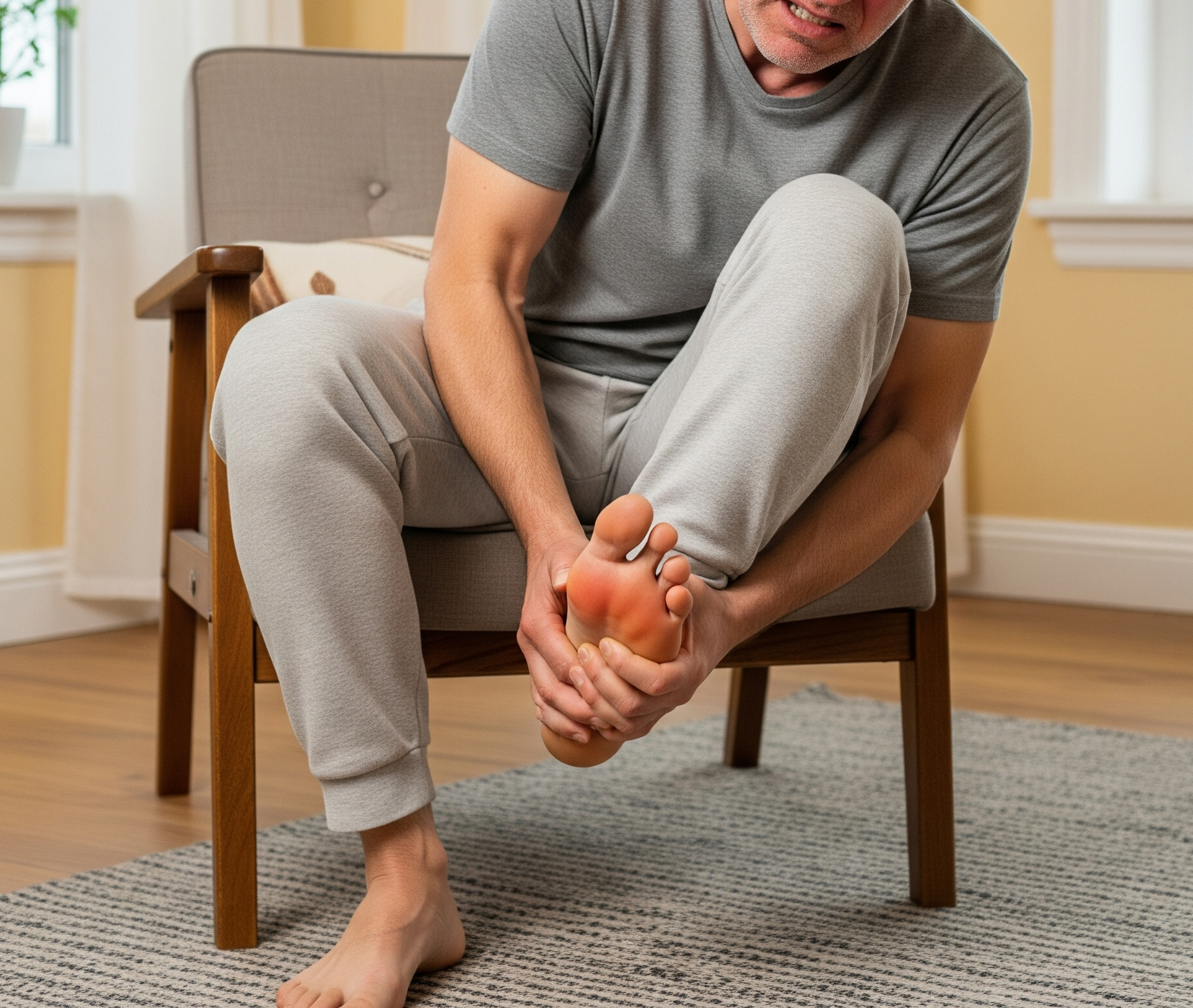 |
A gout flare-up can cause severe pain, swelling, and joint stiffness. Illustration generated by AI. |
Patients can take several measures to limit pain caused by gout and CPPD:
: Applying cold compresses: Resting the joint and applying ice can reduce pain and inflammation.
: Weight management: Maintaining a moderate weight reduces the likelihood of gout attacks. Being overweight can lead to increased inflammation in the body.
: Exercise: Choosing low-impact exercises helps reduce pressure on the joints.
: Limiting purine-rich foods: Red meat, some seafood, organ meats, alcohol, and sugary drinks should be limited to prevent increased uric acid production in the body.
Swelling and pain symptoms caused by gout crystals can be treated with oral or injected medication as advised by a doctor. People with fever and painful, hot joints should see a doctor immediately as these may be signs of infection.
Doctors can diagnose gout or CPPD based on symptoms and joint appearance. Patients can also undergo several tests, such as joint fluid analysis, blood tests to check uric acid levels and other electrolytes (such as calcium, phosphate, magnesium), and ultrasound to help locate crystals in or around the joints.
Anh Ngoc (According to Medical News Today)
| Readers can ask questions about musculoskeletal diseases here for doctors to answer. |