Hepatitis D, caused by the HDV virus, is a liver disease. This virus multiplies and spreads only when the hepatitis B virus (HBV) is present in liver cells. Co-infection with hepatitis B and D elevates the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. To diagnose hepatitis D, doctors may order blood tests to detect the presence of antigens, antibodies, or RNA of the virus in the blood.
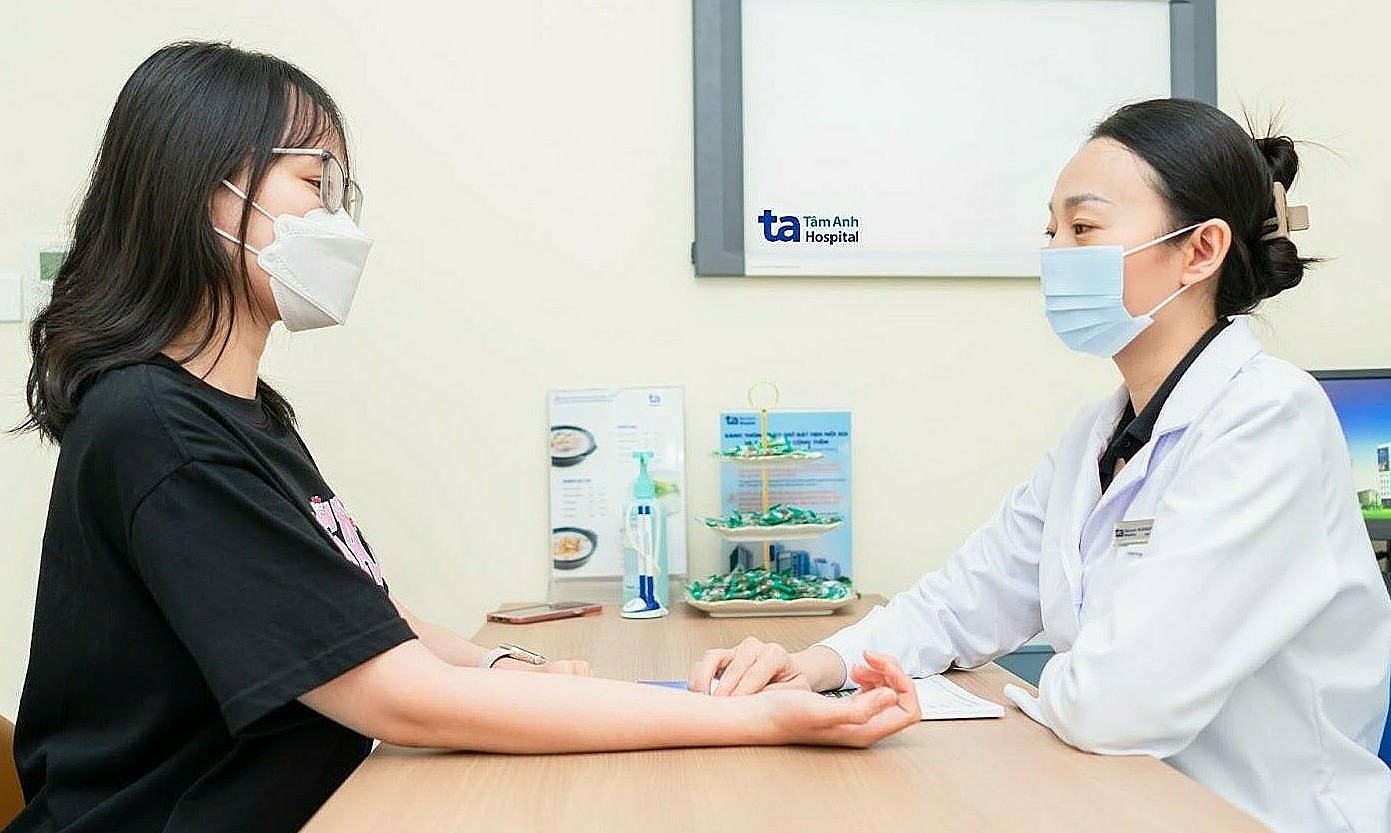 |
Doctor Huyen Van consults a patient. Illustration: Tam Anh General Hospital |
HBc total and HBsAg tests commonly check for hepatitis B virus infection, as the hepatitis D virus only develops if you are already infected with HBV. If the body tests HBsAg positive for hepatitis B, doctors will perform additional tests to determine if the patient also has hepatitis D.
Liver function tests check for liver damage. AST, ALT, and ALP tests assess liver cell damage and bile duct obstruction. Additionally, tests evaluating protein, albumin, coagulation, and bilirubin levels may be ordered for acute hepatitis assessment.
Liver elastography is a non-invasive method that assesses the degree of liver fibrosis. It is important in diagnosing and monitoring chronic liver diseases and supports early detection of complications such as cirrhosis. You should visit a hospital with the aforementioned testing equipment for a doctor to examine you and advise on the appropriate diagnostic method.
Doctor Nguyen Thanh Huyen Van
Department of Gastroenterology
Center for Endoscopy and Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgery
Tam Anh General Hospital TP HCM
| Readers can submit questions about liver disease here for doctors to answer. |