The Tet holiday period often brings changes in environment, weather, and eating habits as people travel or return to their hometowns. These shifts can affect health. Pharmacist Nguyen Thien Dung from the Pharmacy Department at the University Medical Center Ho Chi Minh City advises on essential medications to have readily available during this time.
Fever reducers
Paracetamol is a common pain reliever and fever reducer. Use it when symptoms appear, with a dose of 325-650 mg at least 4 hours apart. The maximum dose is 4 g/day for individuals with normal liver function and 3 g/day for patients with impaired liver function.
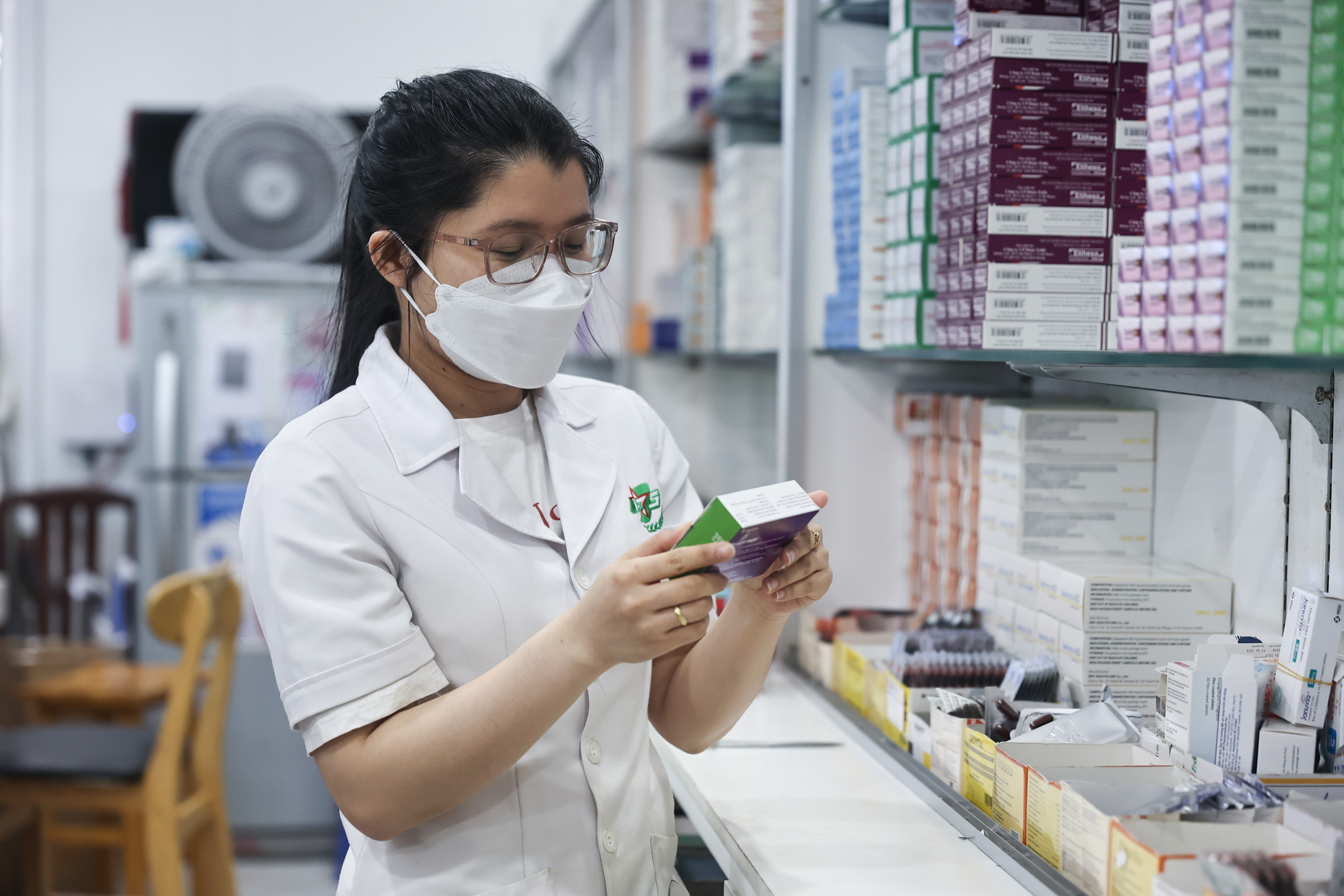 |
Medical staff at Military Hospital 175's pharmacy dispense medicine to a patient. *Photo: Quynh Tran*
Allergy medications
H1 antihistamines like: cetirizine (Zyrtec), levocetirizine (Xyzal), loratadine (Lorastad, Clarityne), desloratadine (Aerius), and fexofenadine (Telfast BD, Telfast HD) treat symptoms such as runny nose, hives, and allergies to food or weather. These medications may cause drowsiness, so exercise caution when driving or operating machinery.
Combination medications
Common combination products include: Tiffy and Decolgen. These combine multiple active ingredients to treat typical cold and flu symptoms such as rhinitis, nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, headache, and fever. Be aware that these products often contain paracetamol. Monitor the dosage carefully when combining them with other paracetamol-containing pain and fever relievers to avoid overdose.
Medications for chronic conditions
Individuals with chronic conditions such as diabetes or hypertension must monitor their blood sugar and blood pressure. Adhere to regular medication schedules and dosages. Additionally, patients should stock enough medication for the holiday period, anticipating that clinics and pharmacies may not yet be fully operational.
Stomach pain medications
Popular antacids include: Kremil-S, Siloxogene, Gastropulgite, Konimag, Trimafort, and Gaviscon. These medications neutralize excess stomach acid, reducing acidity in the stomach and alleviating symptoms of peptic ulcers, heartburn, and gastroesophageal reflux. Take these medications after meals. For suspensions, drink directly or dilute in water. For tablets, chew thoroughly before swallowing.
Digestive aids
Changes in eating habits and alcohol consumption can lead to bloating and indigestion. Keep some digestive enzymes in your medicine cabinet.
Diarrhea medications
Medications containing: diosmectite (Smecta), loperamide (Imodium), attapulgite (Actapulgite), and berberine (Berberine, Berberal) are effective against diarrhea. These work through various mechanisms, such as adhering to and absorbing harmful agents, forming a protective barrier for the digestive lining, antibacterial action, or reducing intestinal motility. It is important to rehydrate and replenish electrolytes if experiencing frequent diarrhea throughout the day. If a patient exhibits symptoms of infection, such as: disorientation, fever, or passing bloody or mucous stools, seek immediate medical advice at the nearest healthcare facility.
Constipation medications
To prevent constipation, drink plenty of water and include more green vegetables and fruits in your diet to stimulate bowel movements and increase stool bulk, making defecation easier. If symptoms significantly impact your quality of life, consider medications such as: sorbitol or lactulose (Duphalac, Laevolac). These products are typically in powder or suspension form; mix them with water and take on an empty stomach.
First-aid supplies
Every family should have essential wound first-aid items, including: adhesive bandages, sterile gauze, and scissors. Readily available solutions for cleaning and disinfecting wounds include: povidone iodine (Povidine, Betadine), hydrogen peroxide, and 70% alcohol.
My Y