Food poisoning in children is an acute illness occurring from consuming food or drinks contaminated with microorganisms, toxins, or chemicals, leading to digestive dysfunction. Early symptoms often include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Severe cases can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or sepsis.
Specialist Tran Pham Thuy Hoa, from the Nutrition Department at Tam Anh General Hospital Hanoi, recommends that parents implement food poisoning prevention measures for children during this period.
Adhere to the "eat cooked, drink boiled" principle
Uncooked food or unhygienic drinking water can harbor bacteria, viruses, parasites, and toxins that cause digestive illnesses. Cooking food at appropriate temperatures destroys these harmful agents, reducing the risk of diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
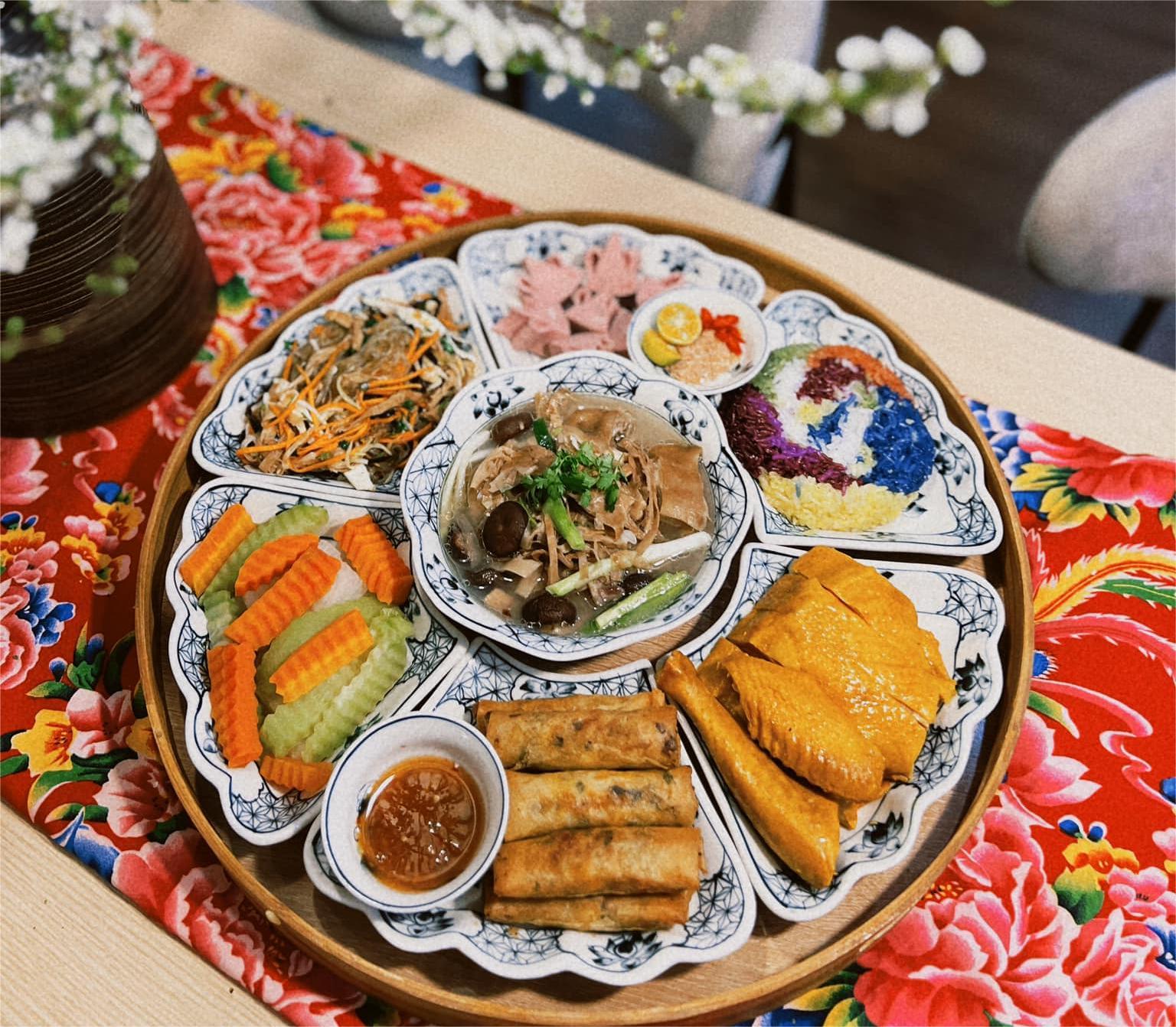 |
Food must be thoroughly cooked before consumption to eliminate the risk of poisoning. *Vinh Gia*
Choose fresh, clean food
Substandard, spoiled food or food containing chemical residues and pathogenic microorganisms increases the risk of digestive disorders and infections. Parents should prioritize selecting food with clear origins, ensuring it is fresh with natural colors and flavors. Limit the use of pre-processed, packaged foods with unclear expiry dates or those stored improperly. Fruits and vegetables must be thoroughly washed, soaked, and prepared correctly.
Proper storage
Cooked food left at room temperature for over two hours creates favorable conditions for bacterial growth and toxin production, harming the digestive system. Cooked dishes should be tightly covered, refrigerated at an appropriate temperature, and consumed within a safe period. Before serving to children, food must be thoroughly reheated to eliminate any remaining microorganisms. Avoid mixing old food with new, or giving children dishes that show signs of spoilage or altered smell.
Hand and utensil hygiene
Hands, cooking, and eating utensils are common vectors for disease-causing bacteria, viruses, and parasites if not properly cleaned. Therefore, it is essential to instill the habit in children of washing their hands with soap before eating and after using the toilet. Adults must also wash their hands thoroughly before preparing food or feeding children. Bowls, spoons, cups, and cooking utensils require thorough washing, hot water rinsing, and dry storage.
Parents should also ensure hygienic conditions to prevent food poisoning and digestive illnesses. Children should eat in clean environments, ideally using their own eating utensils. They should drink certified bottled water or cooled boiled water. Maintaining these hygiene principles during Tet outings helps reduce infection risks and protects children's delicate digestive systems and overall health.
Hang Tran
| Readers can submit questions about neonates here for doctors to answer. |