High blood pressure is a common health issue that can lead to serious complications if not managed. Individuals should regulate blood pressure through a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise. Among various activities, the wall sit exercise offers positive effects.
This exercise allows muscles to contract and extend with minimal joint movement. It primarily targets the thigh muscles, requiring a sustained posture for a specific duration. This builds muscular endurance, improves blood circulation, and enhances vascular flexibility. Consequently, arterial pressure decreases more quickly, which can help stabilize blood pressure.
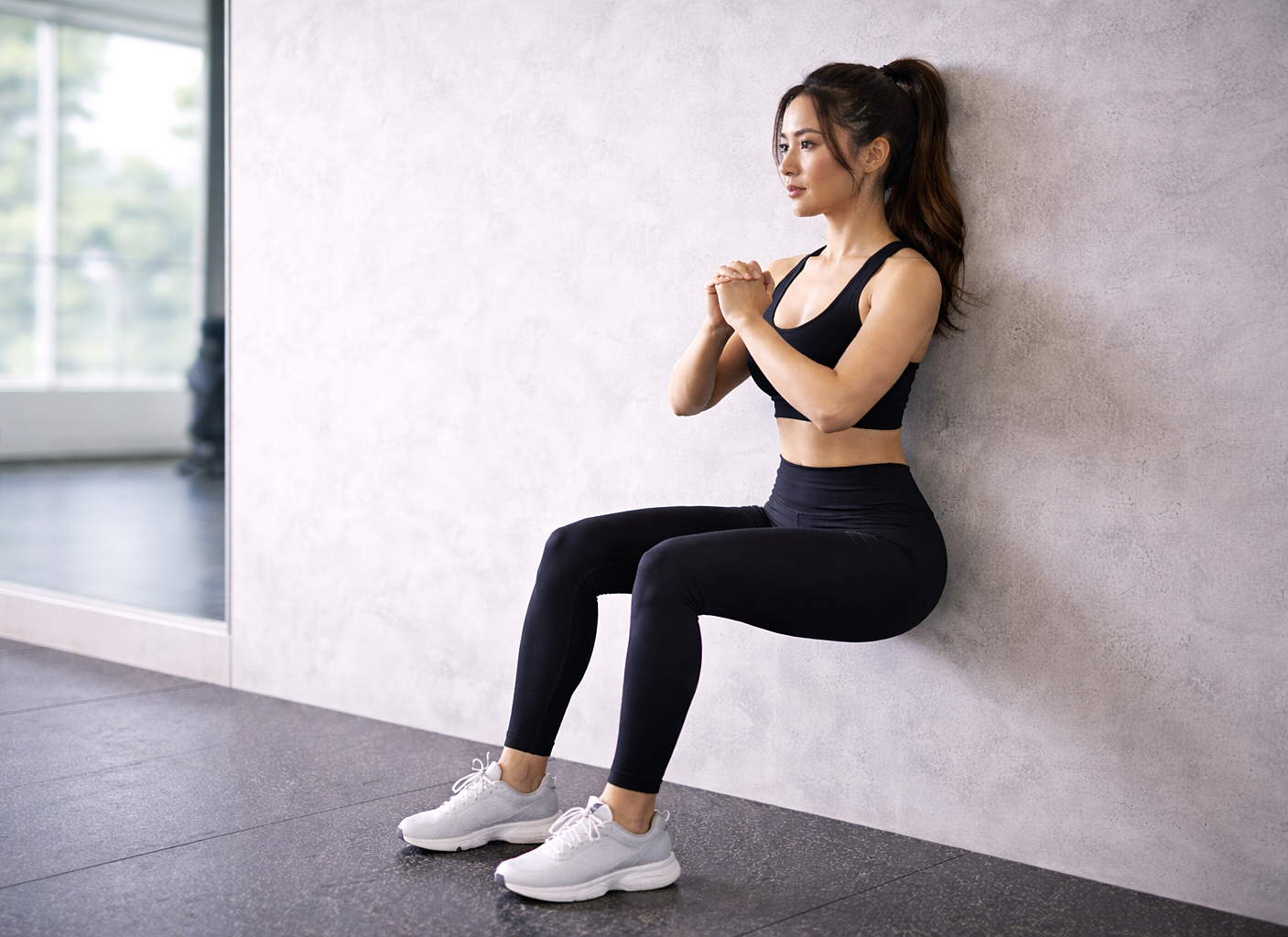 |
The wall sit exercise contributes to reducing high blood pressure. AI-generated image |
To perform the exercise: Stand with your back against a wall, ensuring your knees are bent at a 90-degree angle. Hold this position for about two minutes (or longer, depending on your endurance), then slowly stand up and rest for a few minutes.
Frequency: Practicing this exercise about three times each week can yield optimal results.
Safety notes: This exercise is generally safe for most adults but is not suitable for individuals with knee or back problems. It is an effective way to strengthen the lower body, especially the thighs and glutes. However, incorrect posture or excessive exertion can increase pressure on joints, leading to discomfort, muscle fatigue, or injuries over time.
Notes for individuals with high blood pressure: Patients should avoid sudden high-intensity activities such as sprinting, skydiving, diving, or exercises involving rapid posture changes or breath-holding. These activities can cause blood pressure to spike, straining the heart. Engage in activities within your capacity, warm up thoroughly, and rest if you experience signs of fatigue or dizziness.
Combine with lifestyle changes: To achieve good blood pressure control, integrate the wall sit exercise with a balanced diet, ample hydration, sufficient sleep, stress management, and reduced salt intake. Supplementing with potassium-rich foods, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol also helps. Consult a doctor if you experience symptoms like headache, dizziness, tinnitus, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, fatigue, nausea, or if your blood pressure consistently measures above 140/90 mmHg.
By Le Nguyen (According to Times of India)
| Readers can send cardiovascular questions here for doctors to answer. |