When a headache strikes, finding relief is often the top priority. While triggers vary among individuals, certain foods and drinks are known to worsen headache symptoms or even trigger them. Understanding these potential culprits can help you manage and reduce the severity of your headaches.
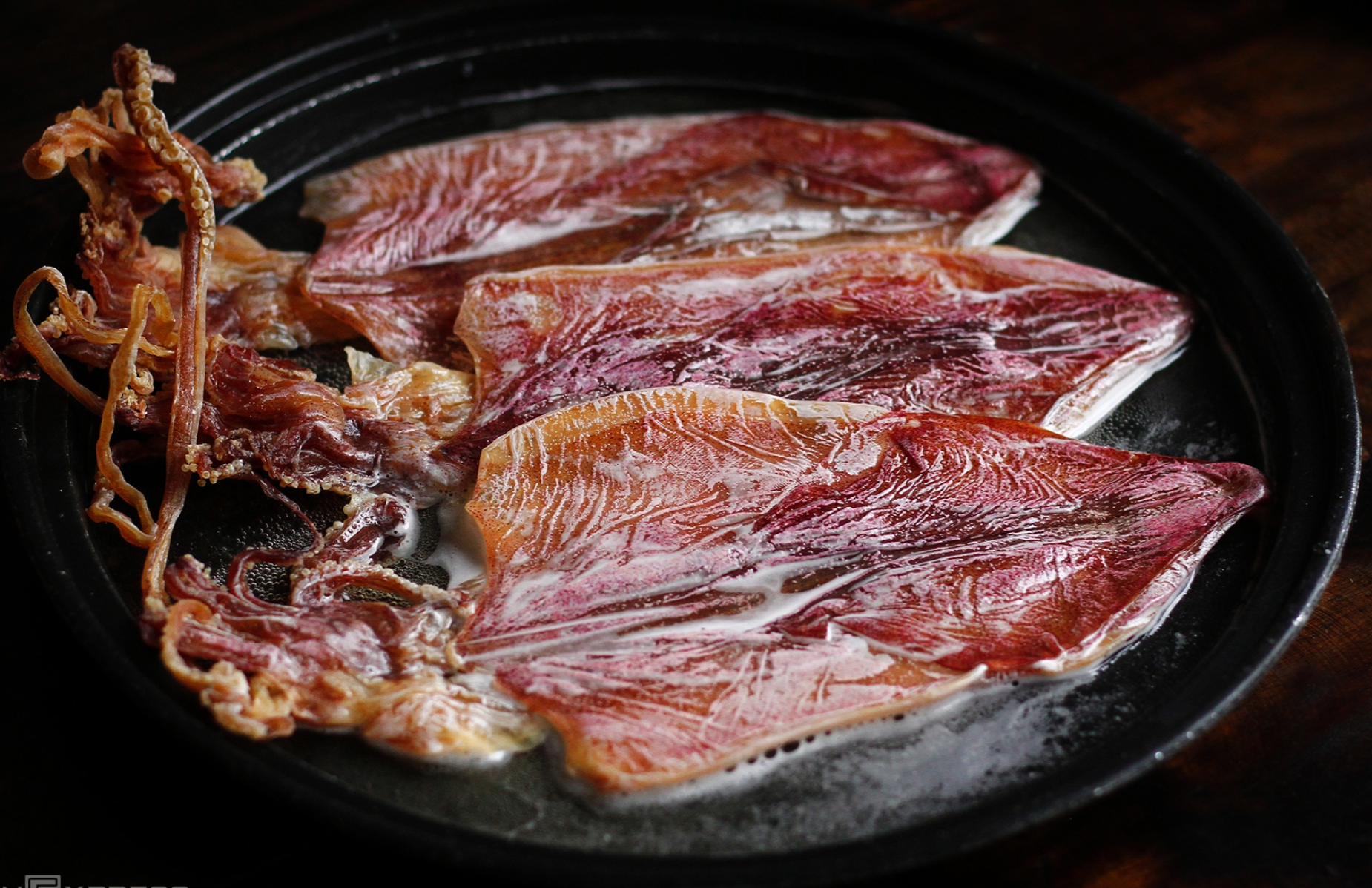 |
Dried squid has a high cholesterol content and is often prepared with high salt content, increasing sodium intake. High sodium consumption can cause water retention, increased blood pressure, or fluid imbalance, which can trigger or worsen headaches, especially in sensitive individuals. |
Dried squid, a popular snack, often contains high levels of cholesterol and is typically prepared with significant salt. This high sodium intake can lead to water retention, elevated blood pressure, or an imbalance of fluids in the body. For sensitive individuals, these physiological changes can easily trigger or intensify headaches.
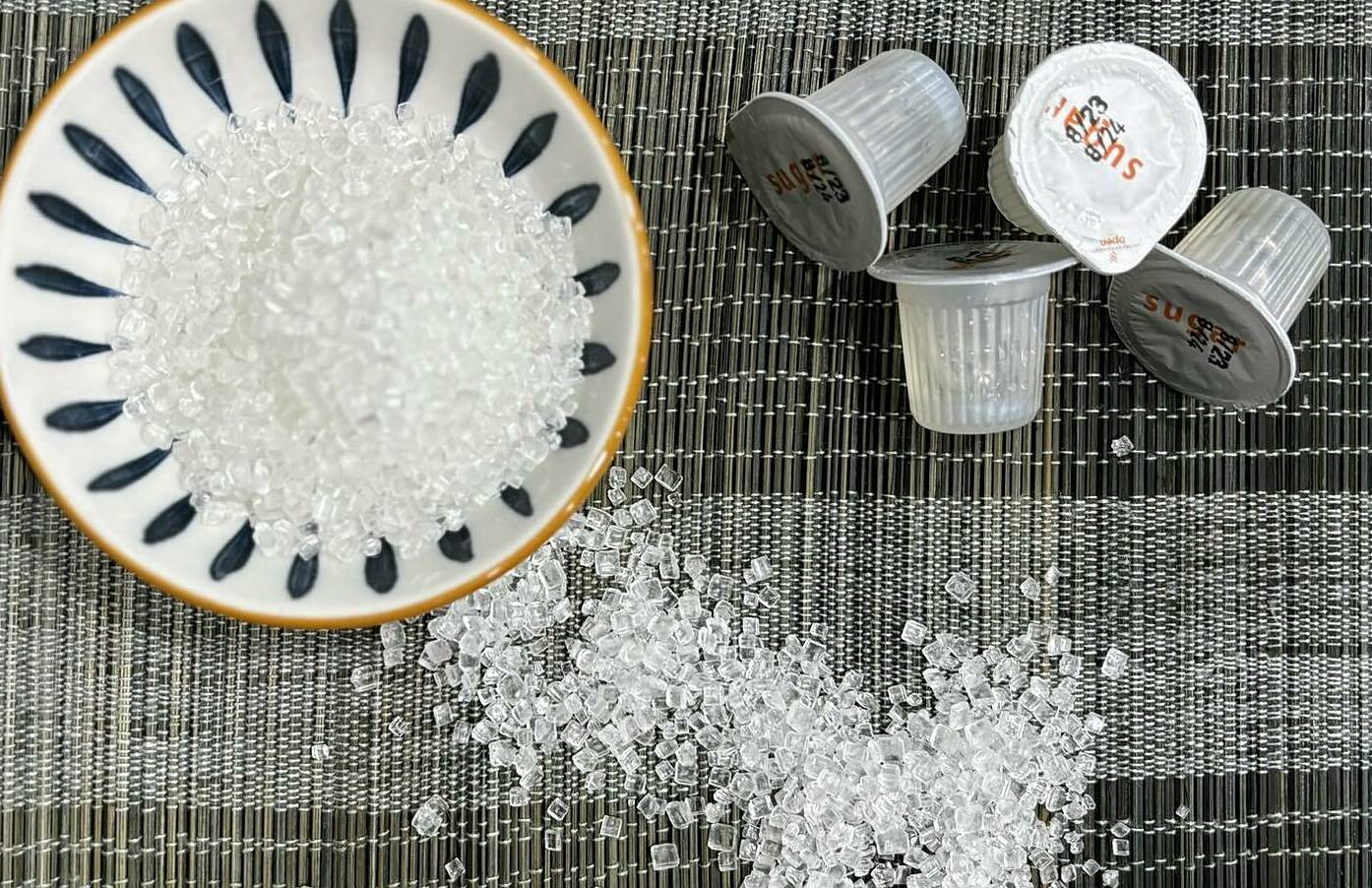 |
Artificial sweeteners like aspartame in sugary drinks can increase the frequency and severity of headaches in some sensitive individuals. Excessive sugar consumption can also increase inflammatory responses and cause blood sugar fluctuations, which can trigger or worsen headaches. These sudden changes can cause abnormal constriction and dilation of brain blood vessels, altering blood flow to the brain and contributing to headaches. |
Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame found in many sugary beverages, can heighten both the frequency and intensity of headaches for some people. Beyond artificial sweeteners, consuming too much regular sugar can also lead to increased inflammatory responses and significant blood sugar fluctuations. These abrupt shifts can cause brain blood vessels to constrict and dilate abnormally, affecting blood flow and contributing to headache onset or worsening.
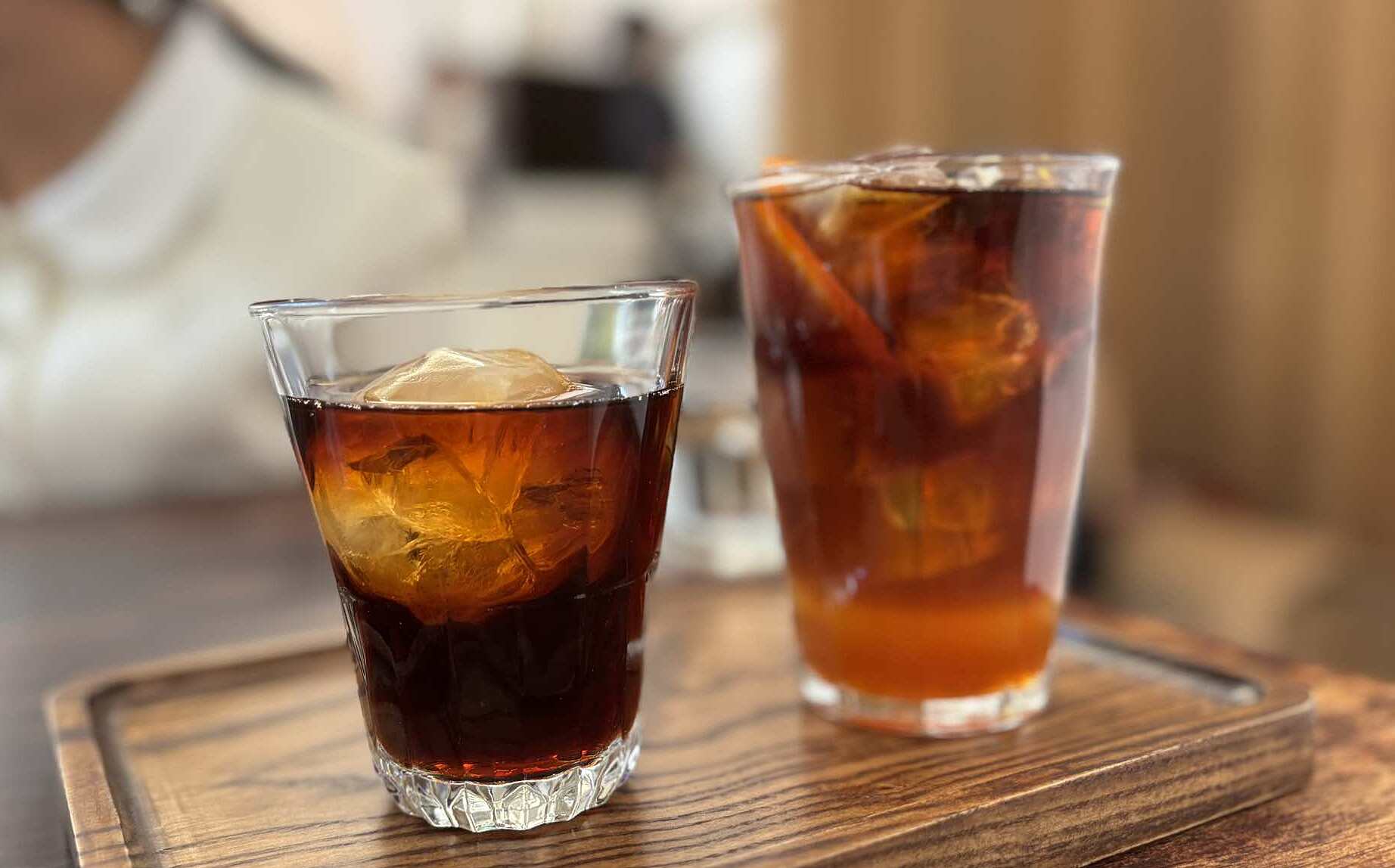 |
Coffee contains caffeine, which has a mild diuretic effect, particularly in those who consume it infrequently. Drinking coffee during a headache can lead to faster dehydration if adequate fluid replacement does not occur. Dehydration can affect blood pressure and blood sugar, worsening headaches. Caffeine-containing drinks can also cause sleep difficulties or reduce sleep quality, prolonging headaches. |
Coffee, with its caffeine content, acts as a mild diuretic, especially for infrequent consumers. If consumed during a headache, it can accelerate dehydration if you do not replenish fluids sufficiently. Dehydration, in turn, impacts blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which can make headaches more severe. Furthermore, caffeine-laden beverages can disrupt sleep or diminish sleep quality, potentially extending the duration of a headache.
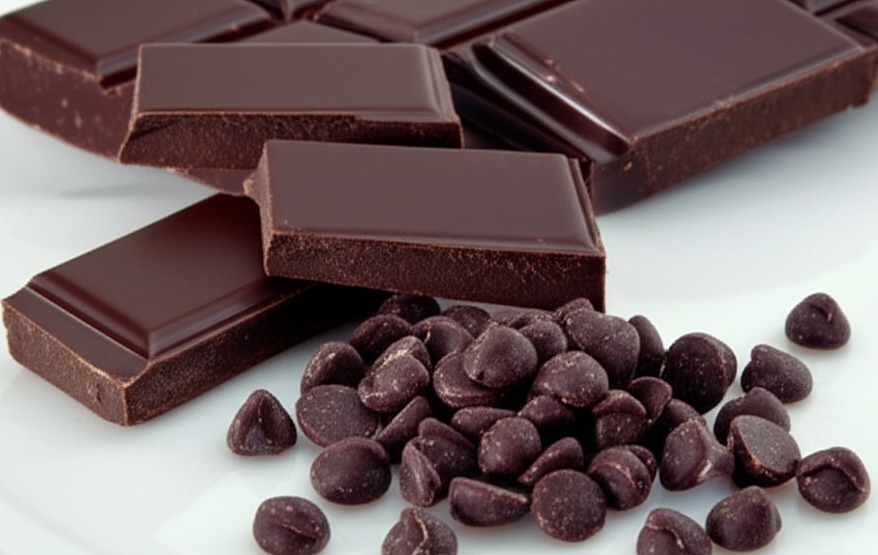 |
While dark chocolate benefits brain health, some individuals should limit it when experiencing a headache. The sugar, caffeine, and tyramine in chocolate can affect brain blood vessel dilation and constriction, which can trigger or make headaches harder to control. |
Dark chocolate offers benefits for brain health; however, some individuals should limit its consumption when experiencing a headache. The combination of sugar, caffeine, and tyramine present in chocolate can influence the dilation and constriction of brain blood vessels. This effect can trigger headaches or make existing ones more challenging to manage.
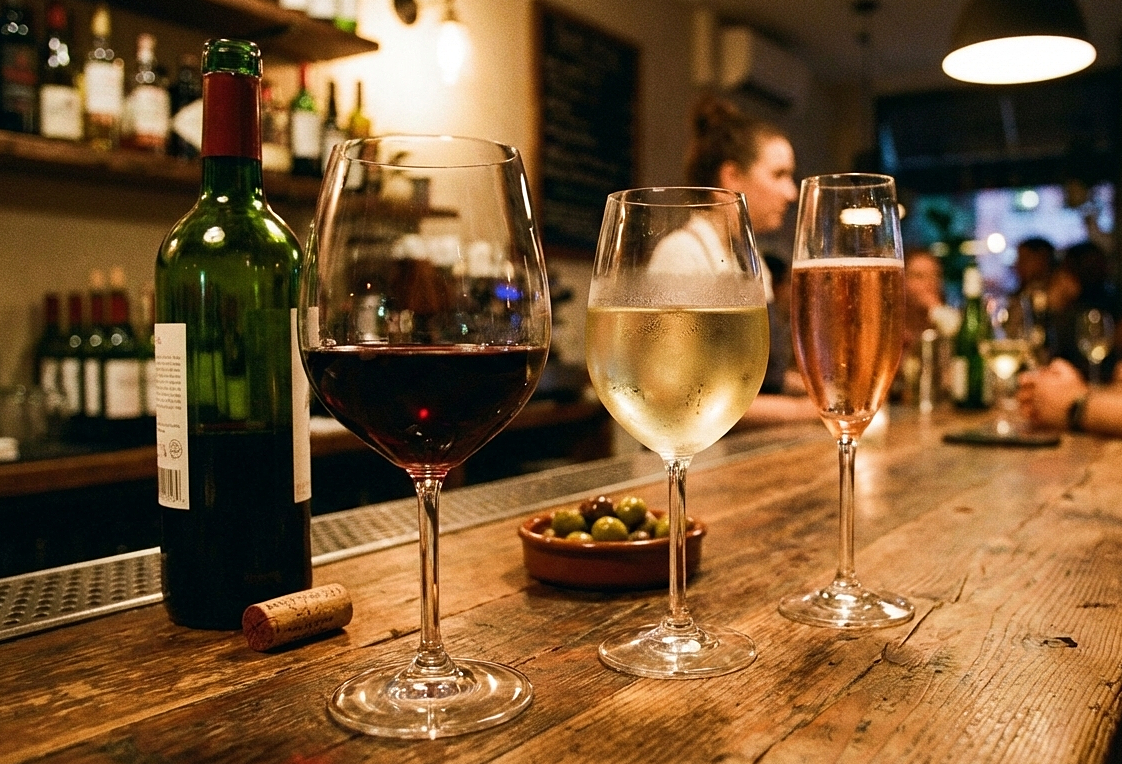 |
Alcohol, containing ethanol, can dilate brain blood vessels, stimulate histamine release, and trigger inflammatory responses, intensifying pain. Alcohol also has diuretic properties, causing dehydration, thirst, and dizziness, which severely worsen headaches. |
Alcohol, specifically its ethanol content, can dilate blood vessels in the brain, stimulate the release of histamine, and provoke inflammatory responses, all of which intensify headache pain. Additionally, alcohol's diuretic properties lead to dehydration, thirst, and dizziness, severely exacerbating headaches.
Anh Chi (According to Very Well Health, Eating Well)
Photos: Bui Thuy, Anh Chi, AI