According to nutritionist Nguyen Thi Thu Huyen from the Department of Nutrition at Tam Anh General Hospital Hanoi, consuming the right carbohydrates provides energy and supports brain function. Here are some carbohydrate options recommended for diabetics:
Brown rice
Unlike finely milled white rice, brown rice retains its bran layer, rich in fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. Its high fiber content slows glucose absorption into the bloodstream, limiting post-meal blood sugar spikes. This sustained feeling of fullness also helps patients manage portion sizes and weight.
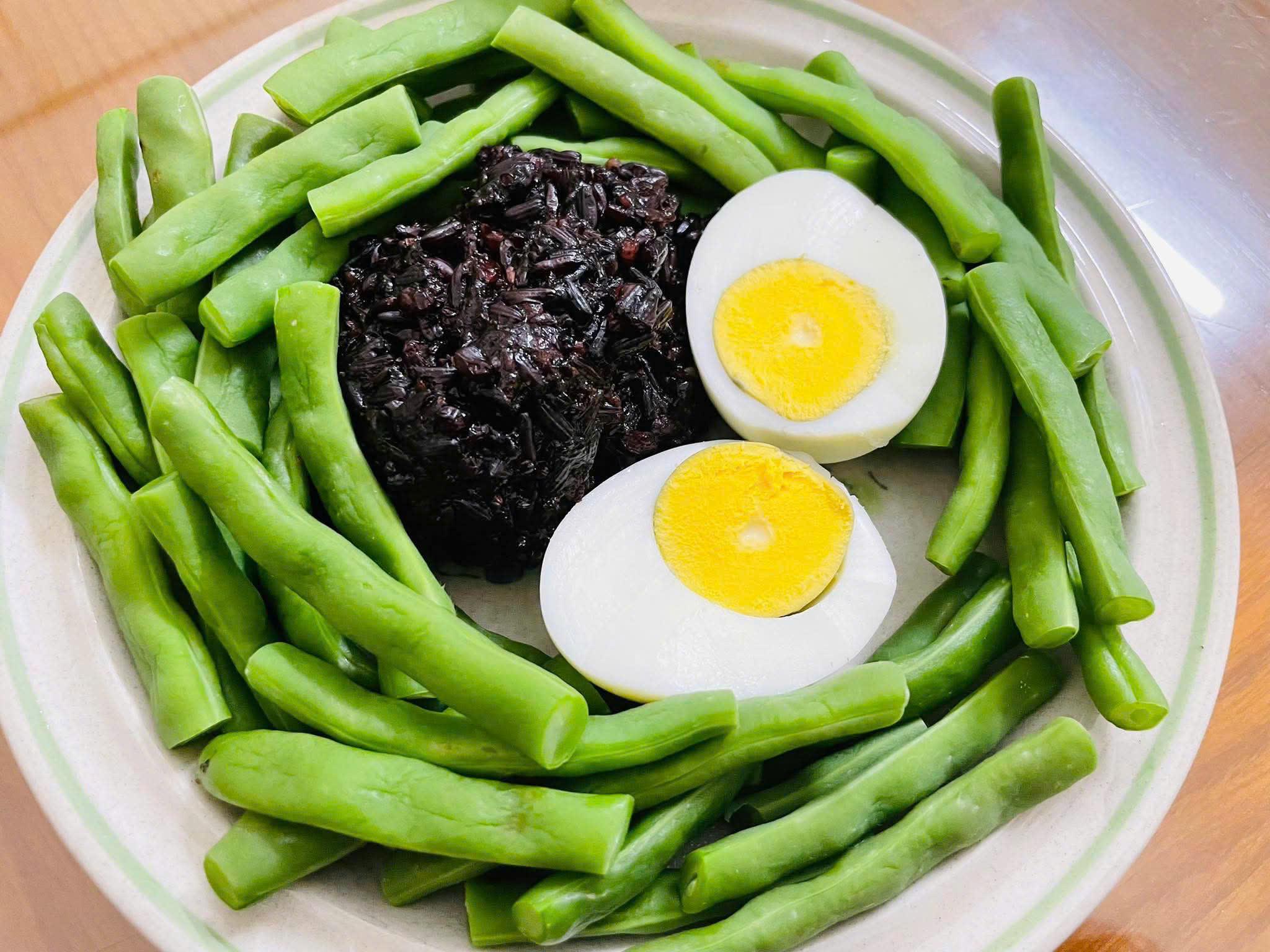 |
Brown rice has a high fiber content that slows down glucose absorption into the blood. Illustration: Thanh Ba |
Whole-grain oats
Whole-grain oats contain beta-glucan, a soluble fiber that slows digestion and stabilizes blood sugar. Oats also reduce blood fat and bad cholesterol, helping prevent cardiovascular disease, a common complication of diabetes. However, patients should distinguish whole-grain oats from processed instant varieties, which often contain added sugar and have a higher glycemic index.
Sweet potatoes
Sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic index than potatoes and white rice, and are rich in fiber, vitamin A, and antioxidants. Diabetics can better manage blood sugar by consuming boiled or steamed sweet potatoes, rather than fried, roasted, or those prepared with sugar and condensed milk. Eating the thoroughly washed skin also boosts fiber intake.
Legumes
Legumes such as green beans, black beans, red beans, lentils, and chickpeas are also healthy carbohydrate sources. The carbohydrates in beans digest slowly, allowing blood sugar to rise gradually and preventing sharp fluctuations after meals. Beans are also rich in plant protein, fiber, and minerals, providing energy and curbing hunger. Incorporating beans into soups, salads, or cooking them with whole grains creates more diverse and balanced meals.
Whole grains
Whole grains like whole-wheat bread, whole-wheat pasta, brown rice vermicelli, and quinoa are also suitable for diabetics. Compared to refined grains, whole-grain products retain most of their fiber and micronutrients. Consequently, they have a low glycemic index, ensuring stable blood sugar control. Quinoa contains all essential amino acids, making it beneficial for diabetics needing to manage weight and blood fat.
Beyond selecting the right carbohydrates, cooking methods significantly impact blood sugar. Overcooked, finely mashed, or fried carbohydrates often cause rapid blood sugar increases. Conversely, boiling, steaming, cooking until just done, and combining them with fiber, protein, and healthy fats will slow glucose absorption. For instance, eating brown rice with green vegetables and steamed fish is far more beneficial than consuming plain white rice.
Nutritionist Huyen advises diabetics to divide their portions, eat at regular times, and monitor post-meal blood sugar to understand their body's response to specific foods. Since individual responses vary, dietary plans require personalization based on a doctor's advice.
Thanh Ba
| Readers can submit their nutrition questions here for doctors to answer. |