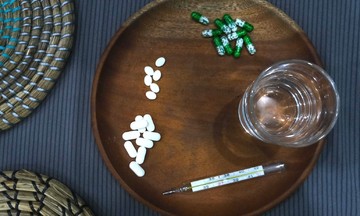Antibiotics are used to inhibit or destroy infection-causing bacteria. Doctor Nguyen Anh Duy Tung, a specialist in nutrition and dietetics at Tam Anh District 7 Polyclinic, notes that these medications can affect the gut microbiota, reduce beneficial bacteria, and cause digestive imbalance. Antibiotic use can lead to bloating, digestive disorders, diarrhea, and even impact liver or intestinal function. During treatment, patients should supplement with appropriate nutrients to support the digestive system and mitigate side effects.
Yogurt
Yogurt contains probiotics, which help replenish and restore the gut microbiota to a balanced state. Beneficial bacteria in yogurt, such as lactobacillus and bifidobacterium, contribute to reducing antibiotic-induced diarrhea. Patients should choose plain or low-sugar yogurt, consuming it at least 2-3 hours after taking antibiotics to avoid reducing the medication's effectiveness.
Garlic
Garlic is rich in prebiotics, a type of indigestible fiber that serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria, thereby helping them thrive. Including a moderate amount of garlic in daily meals can enhance digestion and nutrient absorption.
Boiled eggs
After antibiotic use, the liver needs time to metabolize and repair damaged cells. Protein is a crucial component supporting liver cell regeneration. Boiled eggs are a quality, easily digestible protein source, low in saturated fat, which helps reduce the burden on the liver and provides essential amino acids, supporting the body's recovery post-treatment.
 |
Supplementing with essential nutrients after taking antibiotics helps the digestive system recover. *AI-generated image* |
Fiber-rich foods
Fiber plays a crucial role in nourishing beneficial gut bacteria. After an antibiotic course, patients should increase their intake of fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, nuts, lentils, sprouts, berries, bananas, and broccoli.
Doctor Tung notes that fiber can slow down drug absorption. Therefore, patients should consume these foods several hours after taking medication or after completing their treatment course.
Cocoa
Pure cocoa contains numerous antioxidant polyphenols that act as prebiotic fiber. They promote the growth of beneficial bacteria like lactobacillus and bifidobacterium, while inhibiting some harmful gut bacteria such as clostridia.
To avoid reducing antibiotic effectiveness, Doctor Duy Tung advises patients not to consume alcohol during treatment. Patients should also avoid high-dose calcium and iron supplements concurrently with antibiotics unless prescribed by a doctor. Limit fast food and oily processed foods. If unusual symptoms or digestive disorders persist after antibiotic use, patients should seek medical attention for appropriate consultation and treatment.
Quoc An
| Readers can submit nutrition questions here for a doctor's answer. |