Sacroiliitis is an inflammatory condition affecting one or both sacroiliac joints. These joints, located near the hips, connect the sacrum (the triangular bone at the base of the spine) to the ilium (the large, flaring bone of the pelvis). It is a primary cause of ankylosing spondylitis.
Specialist Doctor Level I Vo Chau Hoang Long from the Orthopedic Trauma Center at Tam Anh General Hospital, TP HCM, states that sacroiliitis pain typically occurs in the lumbar spine, buttocks, and lower back. In some instances, it may extend to the legs, groin, and feet. The condition also presents with other signs, including:
Pain intensifies with prolonged standing, shifting weight to one leg, climbing stairs, running, taking long strides, or rotating the hips. The sensation of sacroiliitis pain varies widely, ranging from a sharp, stabbing feeling to a dull, persistent ache.
Movement limitations include stiffness in the legs after prolonged sitting or standing, difficulty bending, folding, extending, or rotating the legs. The pain can also alter one's gait.
Swelling, warmth, and redness may appear in the inflamed sacroiliac joint region. Patients might also experience a mild fever.
 |
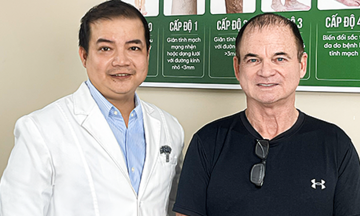
Dr. Long explains the health condition to a patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Dr. Long explains the health condition to a patient. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
Dr. Long notes that sacroiliitis is often challenging to diagnose due to many conditions causing similar pain, such as sciatica, spinal arthritis, or herniated discs. Therefore, upon noticing any warning signs, patients should consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. This approach aims to resolve pain and prevent the condition from becoming chronic.
Doctors typically prioritize pain medication, combined with physical therapy and proper care. This regimen reduces pain, enhances joint strength, flexibility, and mobility, thereby controlling inflammation and mitigating the risk of ankylosing spondylitis. If symptoms do not improve, surgery may be recommended. In some cases, electrical stimulation or shockwave therapy might be prescribed.
Electrical stimulation involves stimulating nerves through the skin and muscles around the sacroiliac joint using high-frequency, progressively intensifying pulsed electrical currents. This method aims to reduce pain, relax muscles, and decrease muscle spasm tone. Shockwave therapy, on the other hand, uses high-energy sound waves to target sensory nerve endings in the sacroiliac joint, promoting bone and soft tissue regeneration after injury and alleviating pain.
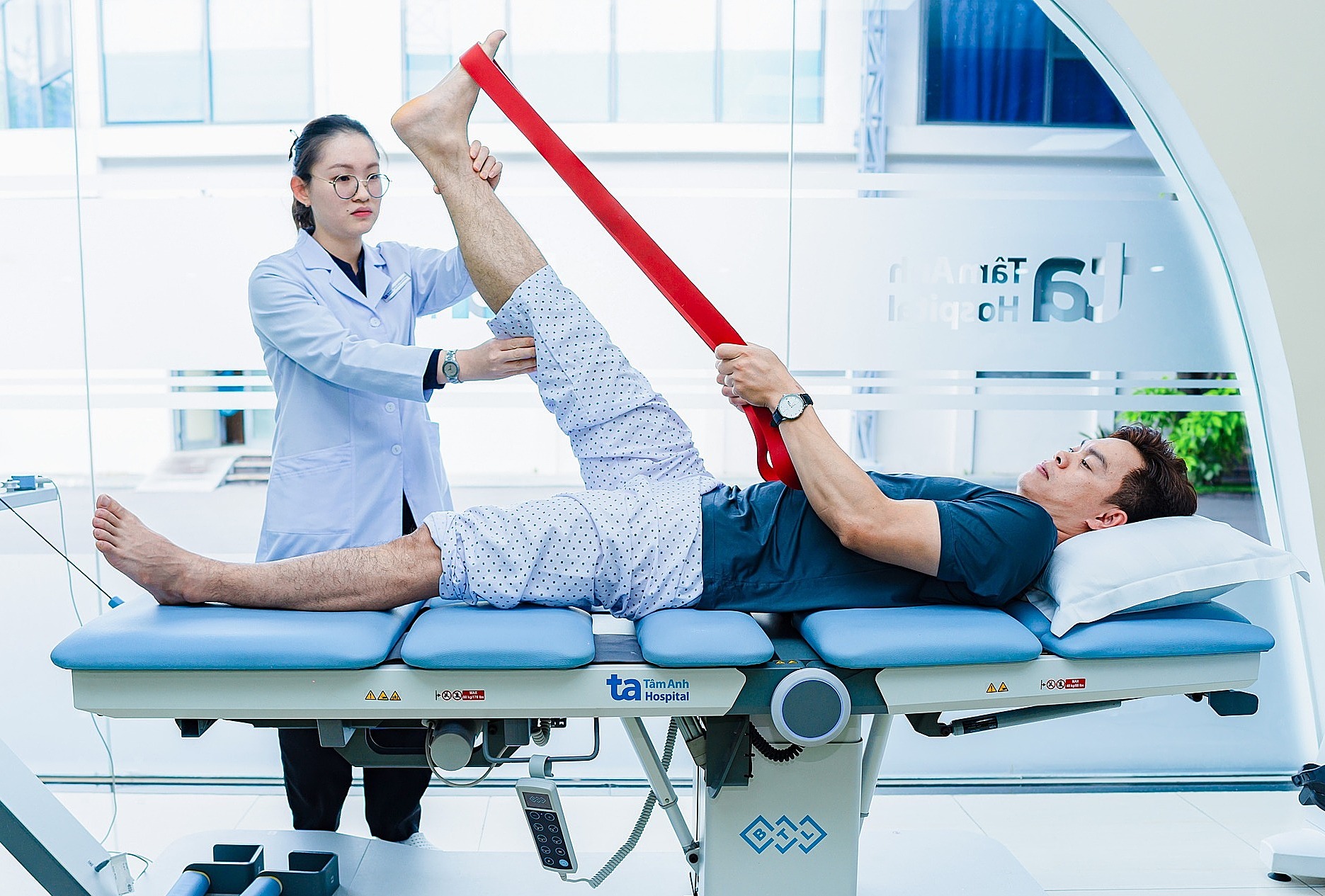 |
A patient performs rehabilitation exercises to improve hip joint muscle strength. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital |
A patient performs rehabilitation exercises to improve hip joint muscle strength. Photo: Tam Anh General Hospital
According to Dr. Long, if not detected and treated properly, sacroiliitis can lead to complications such as muscle atrophy and restricted movement due to widespread damage. This damage can invade the sciatic nerve systems or adjacent muscles like the gluteal and thigh muscles. Extensive damage affecting crucial joints and nerves may result in joint fusion and deformation. Patients may experience limb stiffness, difficulty walking or standing, inability to turn, bend, or sit for extended periods, potentially progressing to paralysis. In women, sacroiliitis can cause complications like salpingitis and cervicitis, impacting fertility, increasing rates of infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and difficult childbirth.
Phi Hong