Answer:
Common symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) include heartburn, vomiting, a burning sensation in the throat, and bad breath. The esophagus and lungs share nerve pathways. When stomach acid refluxes and irritates nerve endings in the esophageal lining, the brain receives signals and activates a self-defense reflex. This results in bronchial smooth muscle contraction, narrowing the airways and leading to breathlessness, shortness of breath, and wheezing.
Bloating and abdominal distension often accompany reflux. This condition pushes the diaphragm, the primary muscle supporting respiration, upwards. This reduces the lungs' expansion space, forcing the patient to breathe with effort.
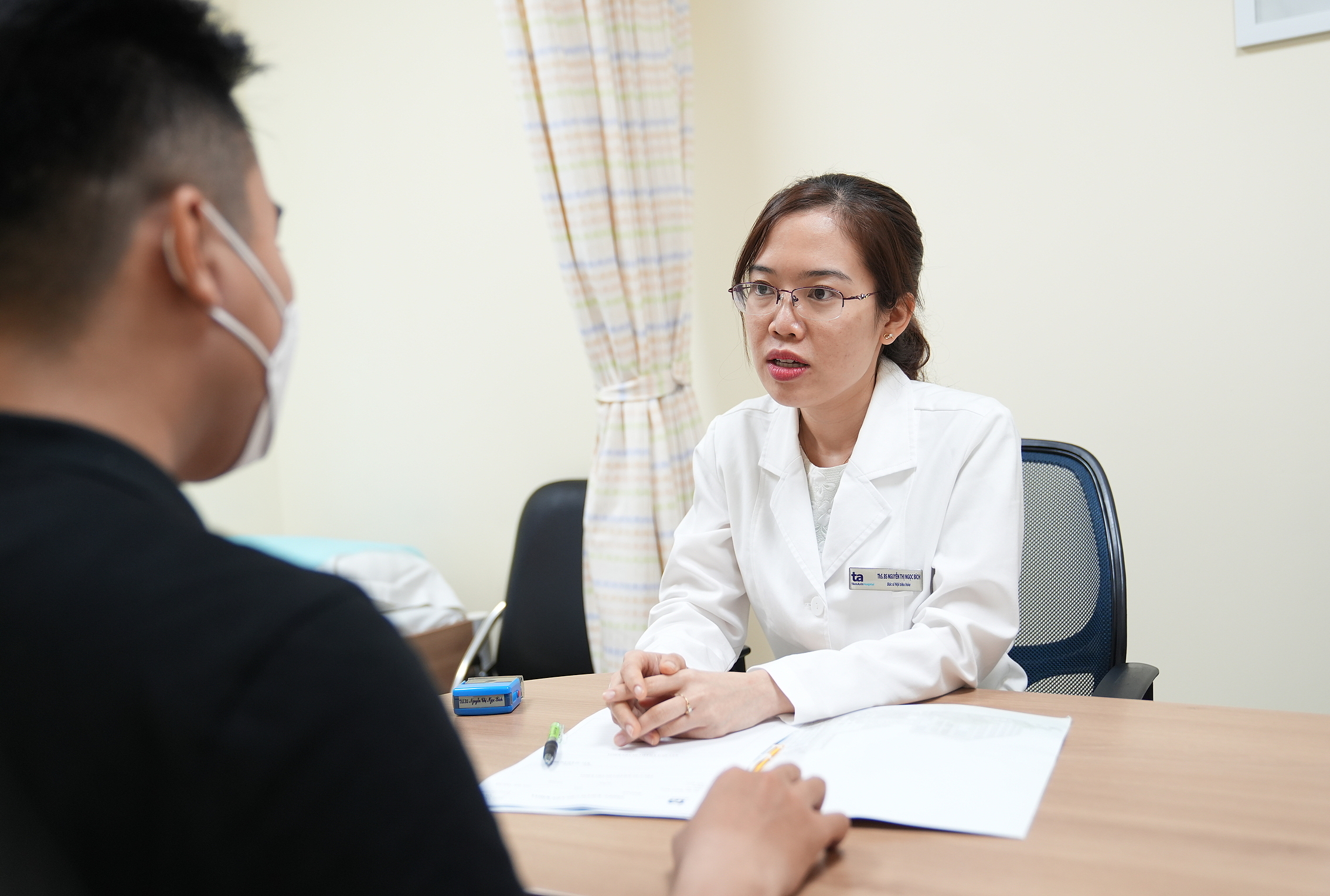 |
Doctor Ngoc Bich consults a patient. Illustration: Tam Anh General Hospital |
Occasional gastroesophageal reflux is not a major concern, but frequent recurrence can signal gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a chronic digestive condition. Individuals with GERD face an increased risk of asthma, airway spasms, and bronchiectasis. These are often accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain and pressure (especially after eating), a chronic cough, wheezing, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing.
You should visit a hospital for examination. Based on the severity of your condition, the doctor will recommend an appropriate treatment plan. This may include lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, weight loss (if overweight or obese), or medication. In cases of complications, patients may undergo other treatments, such as laparoscopic fundoplication surgery.
Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Ngoc Bich
Department of Gastroenterology
Center for Endoscopy and Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgery
Tam Anh General Hospital TP HCM
| Readers can submit questions about digestive diseases here for doctors to answer. |